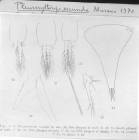
WoRMS name details
Pleurerythrops secunda Murano, 1970
226923 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:226923)
unaccepted (Incorrect gender ending)
Species
marine, fresh, terrestrial
Murano, M. (1970). A small collection of benthic Mysidacea from coastal waters in Suruga Bay, Japan. <em>Crustaceana.</em> 18: 251-268. [details] Available for editors  [request]
[request]
Depth range 28-240m
Taxonomic remark Email from Karl Wittmann to Jan Mees dd 8-9-2015: Many species names of Erythropinae are badly spelled. In those cases...
Depth range 28-240m [details]
Taxonomic remark Email from Karl Wittmann to Jan Mees dd 8-9-2015: Many species names of Erythropinae are badly spelled. In those cases...
Taxonomic remark Email from Karl Wittmann to Jan Mees dd 8-9-2015: Many species names of Erythropinae are badly spelled. In those cases where the genus name ends with "-ops" and the species name is an adjective, the name has to be transferred from female to male gender. [details]
Mees, J.; Meland, K. (Eds) (2012 onwards). World List of Lophogastrida, Stygiomysida and Mysida. Pleurerythrops secunda Murano, 1970. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=226923 on 2024-09-21
![]() The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License
The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License
original description
Murano, M. (1970). A small collection of benthic Mysidacea from coastal waters in Suruga Bay, Japan. <em>Crustaceana.</em> 18: 251-268. [details] Available for editors  [request]
[request]
basis of record Price, W. (2001). World list of Mysidacea. [details]
additional source Müller, H. G. (1993). World catalogue and bibliography of the recent Mysidacea. 238p. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Pillai, K.N. (1973). Mysidacea of the Indian Ocean. handbook to the International Zooplankton Collections 4; p.1-125; Indian Ocean Biological Centre; Kerala state, India [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Hansen, H.J. (1910). The Schizopoda of the Siboga Expedition. -. <em>Siboga Exped., 37: 1-123, pls. 1-16.</em> [details]
additional source Holt, E. W. L.; Tattersall, W. M. (1906). Schizopodous Crustacea from the north-east Atlantic slope. <em>Supplement. Fisheries, Ireland, Sci. Invest. 1904.</em> V: 1-50, plates I-V. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source II, N. (1964). Fauna Japonica, Mysidae (Crustacea). <em>Biogeogr. Soc. Japan.</em> 610pp. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Kathman, R.D., W.C. Austin, J.C. Saltman & J.D. Fulton (1986): Identification manual of the Mysidacea and Euphausiacea of the northeast Pacific. - Can. Spec. Publ. Fish. Aquat.Sci., 93: 1-411 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Nouvel, H.; Lagardère, J. P. (1976). Les Mysidacés du talus continental du golfe de Gascogne I. Tribu des Erythropini (genre Erythrops excepté). <em>Bulletin du Muséum National d´Histoire Naturelle.</em> 414 (291): 1243-1324. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Sars, G.O. (1869). Undersøgelser over Christiania-fjordens Dybvansfauna anstillede paa en i Sommeren 1868 foretagen Zoologisk Reise. <em>Nyt Magazin for Naturvidenskaberne.</em> 16: 305-362. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Tattersall, O. S. (1965). Report on a small collection of Mysidacea from the northern region of the Malacca Strait. <em>Journal of Zoology, London.</em> 147: 75-98. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Tattersall, W.M.; Tattersall, O.S. (1951). The British Mysidacea. <em>Ray Society, London.</em> 1-460, figs. 1-118. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Zimmer C. (1909): Die nordischen Schizopoden. K. Brandt & C. Apstein (eds.), Nordisches Plankton. Lipsius und Tischler, Kiel und Leipzig, 6: 1-178 [details]
additional source Bacescu, M.; Iliffe, T. M. (1986). Contribution to the knowledge of Mysidacea from western Pacific: Aberomysis muranoi n.gen., n.sp. and Palaumysis simonae n.gen., n.sp. from marine caves onPalau, Micronesia. <em>Trav. Mus. Hist. nat. "Grigore Antipa".</em> 28: 25-35. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Birstein, J.A. & Tchindonova, J.G. (1958). Glubokovodnye mizidy severo-zapadnoi chasti Tikhogo Okeana (Deep-sea mysids of the northwest Pacific Ocean). <em>Trudy Instituta Okeanologii AN SSSr.</em> 27: 258-355. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Brattegard, T. (1969). Marine biological Investigations in the Bahamas 10. Mysidacea from shallow water in the Bahamas and southern Florida. Part 1. <em>Sarsia.</em> 39: 17-106. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Czerniavsky, V. (1882). Monographia Mysidarum inprimis Imperii Rossici. Fasc. 1, 2. <em>Trudy Sankt-Peterburgskago Obshchestvo Estestvoispytatelei (Travaux de la Société des Naturalistes de St.-Pétersbourg).</em> 12: 1-170; 13: 1-85, 4 pls., available online at https://play.google.com/books/reader?id=BXlBAQAAMAAJ&pg=GBS.PP6 [details]
additional source Hansen, H.J. (1908). Crustacea Malacostraca. I. <em>The Danish Ingolf-Expedition.</em> 3 (2): 1-120: pls. 1-5. [details]
additional source Holt, E.W.L.; Tattersall, W.M. (1905). Schizopodous Crustacea from the north-east Atlantic slope. In: Report on the Sea and Inland Fisheries of Ireland in 1902 and 1903. Part II. Scientific Investigations, pp. 99-152, pls 1-11. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Mauchline, J.; Murano, M. (1977). World list of the Mysidacea, Crustacea. <em>J. Tokyo Univ. Fish.</em> 64 (1): 39-88. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Sars, G.O. (1870). Carcinologiske Bidrag til Norges Fauna. I. <em>Monographi over de ved Norges Kyster forekommende Mysider. Pt. 1 Christiania, K. Norske Viidenskab. Trondhjem.</em> 64 pp., pls. I-V. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Sars, G. O. (1879). Carcinologiske Bidrag til Norges fauna. I. <em>Monographi over de ved Norges Kyster forekommende Mysider. Pt. 3. Christiania, A.W. Brøgger.</em> pp. 1-131, 42 pls. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Tattersall, O. S. (1955). Mysidacea. <em>Discovery Rep.</em> 28: 1-190. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Tattersall, W. M. (1939). The Euphausiacea and Mysidacea of the John Murray Expedition to the Indian Ocean. <em>Sci. Rep. John Murray Exped.</em> 5: 203-246. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Tattersall, W. M. (1951). A review of the Mysidacea of the United States National Museum. <em>Smithsonian Institution United States National Museum Bulletin.</em> 201: 1-292., available online at https://play.google.com/store/books/details?id=-vhMAAAAYAAJ&rdid=book--vhMAAAAYAAJ [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Stephensen, K. (1938). Euphausiacea, Mysidacea, Cumacea, and Nebaliacea. <em>In: Jensen, Ad. S., et al., (eds.), The zoology of Iceland. Copenhagen and Reykjavik, Levin & Munksgaard.</em> 3 (29): 1-24,1pl. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Brattegard, T.; Meland K. (1997). Mysidacea (Crustacea) in the Faroe Area. <em>Frodskaparrit.</em> 45: 69-95. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Price, W. (2001). Mysida Bibliography. <em>Internet.</em> [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Brattegard, T. & Vader, W. (1972). A collection of Peracarida from Möre and Romsdal, Northwestern Norway. <em>Sarsia.</em> 49(1): 33-40. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source BRANDT, A. (1997). Biodiversity of peracarid crustaceans (Malacostraca) from the shelf down to the deep arctic Ocean. <em>Biodiversity and conservation.</em> 6(11): 1533-1556. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Wooldridge, T. H.; Mees, J. (2011 onwards). World List of the Mysidacea. [details]
additional source De Roa, E. Z.; Delgado, M. (1989). Pleurerythrops americana, a new species of mysidacea from the coast of Venezuela. <em>Sarsia.</em> 74(2): 91-93., available online at https://doi.org/10.1080/00364827.1989.10420526 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Murano, M. (1981). Mysidacea from the central and western Pacific. 5. Genera Heteroerythrops, Meierythrops, Pleurerythrops, Gibberythrops, Illigiella, Dactylamblyops, Pseudamblyops, Paramblyops, Dactylerythrops and Nakazawai (tribe Erythropini). <em>Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory.</em> 26(4/6): 261-302. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Murano, M. (1970). A small collection of benthic Mysidacea from coastal waters in Suruga Bay, Japan. <em>Crustaceana.</em> 18: 251-268. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Panampunnayil, S.U. 1977. Three new species of Mysidacea from Kerala coast. Pages 28-35, In: Proceedings of the Symposium on Warm Water Zooplankton. National Institute of Oceanography, Goa, India. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Panampunnayil, S.U. (1998). Descriptions of Indoerythrops typicus gen. Nov., sp. Nov. And Pleurerythrops inscita new record from Indian Waters (Crustacea: Mysidacea). <em>Journal of Plankton Research.</em> 20(4): 619-629. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Wittmann, K.J. (2001). Centennial changes in the near-shore mysid fauna of the Gulf of Naples (Mediterranean Sea), with description of <i>Heteromysis riedli</i> sp. n. (Crustacea, Mysidacea). <em>Marine Ecology.</em> 22(1-2): 85-109. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Illig, G. (1930). Die Schizopoden der deutschen Tiefsee-Expedition. <em>Rep. Valdivia Exped.</em> 22: 397-625. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Neyt, K. (2002). Morfologische studie van een nieuwe soort van de ordo Mysidacea uit de Westelijke Indische Oceaan. Unpublished manuscript, Institute voor Dierkunde, Universiteit Gent, Mariene Biologie. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Nouvel, H. (1949). Mysidacea. <em>In: Jespersen, P., & F.S. Russell (eds.), Fiches d´Identification du Zooplankton. Copenhagen. Conseil Permanent International pour l´Exploration de la Mer.</em> [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Stephensen, K. (1933). The Godthaab expedition 1928. Schizopoda. <em>Meddel. Grønland.</em> 79 (9): 1-20. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Astthorson, O. S. (1984). The distribution and biology of mysids in Icelandic subarctic waters as demonstrated by analysis of cod stomach contents. <em>Sarsia.</em> 69 (2): 107-116. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Astthorson, O. S. (1985). Mysids occuring in the stomachs of cod caught in the Atlantic water south and west of Iceland. <em>Sarsia.</em> 70 (2-3): 173-178. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Bacescu, M. (1941). Les Mysidacés des eaux méditerranéennes de la France (spécialement de Banyuls) et des eaux de Monaco. <em>Bull. Inst. Océanogr.</em> 795: 1-46. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source COLOSI, G. (1929). I Misidacei del Golfo di Napoli. Pubbl. Staz. Zool. Napoli, 29: 405-441 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source COLOSI, G. (1930). Remarques sur la distribution horizontale et verticale des mysidés mediterranéens. - Bull. Soc. Océnogr. France, 10: 983-985 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source CUNHA, M.R. & JORBE J.C. & BERNARDES C. (1997). On the structure of the neretic suprabenthic communities from the Portugese continental margin Marine Ecology progress series 157: 119-137 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source ELIZALDE, M. & DAUVIN, J-C & SORBE J-C (1991). Las comunidades suprabentonicas batiales del golfa de Vizcaya (margen sur del canon de cap-ferret): composicion faunitica y estructura [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source ELIZALDE, M. & DAUVIN, J-C & SORBE J-C (1991). Les Mysidacés suprabenthiques de la marge sud du Canyon du cap-ferret (Golfe de Gascogne): répartition bathymétrique et activité natatoire Ann. Inst. Océanogr. 67 (2): 129-144 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source ELIZALDE M.Répartition bathymétrique et activité natatoire près du fond des mysidacés suprabenthiques de la marge sud du canyon du cap-ferret (Golfe de Gascogne) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Hansen, H.J. (1910). Revideret Fortegnelse over Danmarks marine Arter af Isopoda, Tanaidacea, Cumacea, Mysidacea og Euphausiacea. <em>Videnskabelige Meddelelser fra den Naturhistorisk Forening i København.</em> 1909: 197-289., available online at http://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/35855695 [details]
additional source HARGREAVES, P.M. (1985). The distribution of Mysidacea in the open ocean and Atlantic Ocean during 1979. - J. Plankton Res., 7 (2): 241-261. [ecology [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source HOLT, E.W.L. & W.I. BEAUMONT (1900). Survey of fishing-grounds, west coast of Ireland, 1890-1891. X. Report on the Crustacea Schizopoda of Ireland. - Sci. Trans. r. Dublin Soc.,N.S., 7: 223692352,1pl [details]
additional source Lagardère, J.-P. (1985). Biogéographie et composition taxonomique du peuplement abyssal de Mysidacés. <i>In</i>: Laubier, L.; Monniot, Cl., (eds) Peuplement profonds du Golfe de Gascogne: 630 p,. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source MAUCHLINE, J. (1971). Seasonal occurence of mysids (Crustacea) and evidence of social behaviour. - J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K., 51: 809-825. [biology, ecology [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source MURANO, M. (1970). Systematic and ecological studies on Mysidacea collected by the bottom-net. - J. oceanogr. Soc. Japan, 26: 137-150. [ecology [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Murano, M. (1977). Mysidacea from the Central and Western Pacific IV. Genera Euchaetomera, Euchaetomeropsis, Arachnomysis, Echinomysides, Meterythrops and Nipponerythrops (tribe Erythropini). <em>Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory.</em> 24 (1/3): 141-192. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Pillai, N. K. (1965). A review of the work of shallow-water Mysidacea of the Indian waters. <em>Proc. Symposium Crust.</em> 5: 1681-1728. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Ruiyu, L. & Shaowu, W. (1986). Studies of the Mysinae (Crustacea, Mysidacea) of the northern South China Sea. <em>Studia Marina Sinica.</em> 26: 159-202. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source STEPHENSEN, K. (1943). The zoology of East Greenland. Leptostraca, Mysidacea, Cumacea, Tanaidacea, Isopoda and Euphausiacea. - Medd. om Grønland, 121 (10): 1-82 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source TATTERSALL, O.S. (1957). Discovery reports issued by the national Institute of Oceanography Cambridge University press volume XXVII [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source TATTERSALL, W.M. (1909). The Schizopoda collected by the "Maia" and "Puritan" in the Mediterranean. Mitt. zool. Stn. Neapel, 19: 117-143 [details]
additional source Zimmer, C,. (1914). Die Schizopoden der deutschen Südpolar-Expedition 1901-1903. In: von Drygalski (ed.), Deutsche Südpolar-Expedition 1901-1903,. 15, Zool., 7: 377-445. [details]
additional source Murano, M.; Krygier, E. (1985). Bathypelagic mysids from the northeastern Pacific. <em>J. Crust. Biol.</em> 5(4): 686-706. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Hanamura, Y.; Kase, T. (2002). Marine cave mysids of the genus Palaumysis (Crustacea: Mysidacea), with a description of a new species from the Philippines. <em>Journal of Natural History.</em> 36: 253-263. (look up in IMIS), available online at https://doi.org/10.1080/00222930010004241 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
basis of record Price, W. (2001). World list of Mysidacea. [details]
additional source Müller, H. G. (1993). World catalogue and bibliography of the recent Mysidacea. 238p. [details] Available for editors
additional source Pillai, K.N. (1973). Mysidacea of the Indian Ocean. handbook to the International Zooplankton Collections 4; p.1-125; Indian Ocean Biological Centre; Kerala state, India [details] Available for editors
additional source Hansen, H.J. (1910). The Schizopoda of the Siboga Expedition. -. <em>Siboga Exped., 37: 1-123, pls. 1-16.</em> [details]
additional source Holt, E. W. L.; Tattersall, W. M. (1906). Schizopodous Crustacea from the north-east Atlantic slope. <em>Supplement. Fisheries, Ireland, Sci. Invest. 1904.</em> V: 1-50, plates I-V. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source II, N. (1964). Fauna Japonica, Mysidae (Crustacea). <em>Biogeogr. Soc. Japan.</em> 610pp. [details] Available for editors
additional source Kathman, R.D., W.C. Austin, J.C. Saltman & J.D. Fulton (1986): Identification manual of the Mysidacea and Euphausiacea of the northeast Pacific. - Can. Spec. Publ. Fish. Aquat.Sci., 93: 1-411 [details] Available for editors
additional source Nouvel, H.; Lagardère, J. P. (1976). Les Mysidacés du talus continental du golfe de Gascogne I. Tribu des Erythropini (genre Erythrops excepté). <em>Bulletin du Muséum National d´Histoire Naturelle.</em> 414 (291): 1243-1324. [details] Available for editors
additional source Sars, G.O. (1869). Undersøgelser over Christiania-fjordens Dybvansfauna anstillede paa en i Sommeren 1868 foretagen Zoologisk Reise. <em>Nyt Magazin for Naturvidenskaberne.</em> 16: 305-362. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Tattersall, O. S. (1965). Report on a small collection of Mysidacea from the northern region of the Malacca Strait. <em>Journal of Zoology, London.</em> 147: 75-98. [details] Available for editors
additional source Tattersall, W.M.; Tattersall, O.S. (1951). The British Mysidacea. <em>Ray Society, London.</em> 1-460, figs. 1-118. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Zimmer C. (1909): Die nordischen Schizopoden. K. Brandt & C. Apstein (eds.), Nordisches Plankton. Lipsius und Tischler, Kiel und Leipzig, 6: 1-178 [details]
additional source Bacescu, M.; Iliffe, T. M. (1986). Contribution to the knowledge of Mysidacea from western Pacific: Aberomysis muranoi n.gen., n.sp. and Palaumysis simonae n.gen., n.sp. from marine caves onPalau, Micronesia. <em>Trav. Mus. Hist. nat. "Grigore Antipa".</em> 28: 25-35. [details] Available for editors
additional source Birstein, J.A. & Tchindonova, J.G. (1958). Glubokovodnye mizidy severo-zapadnoi chasti Tikhogo Okeana (Deep-sea mysids of the northwest Pacific Ocean). <em>Trudy Instituta Okeanologii AN SSSr.</em> 27: 258-355. [details] Available for editors
additional source Brattegard, T. (1969). Marine biological Investigations in the Bahamas 10. Mysidacea from shallow water in the Bahamas and southern Florida. Part 1. <em>Sarsia.</em> 39: 17-106. [details] Available for editors
additional source Czerniavsky, V. (1882). Monographia Mysidarum inprimis Imperii Rossici. Fasc. 1, 2. <em>Trudy Sankt-Peterburgskago Obshchestvo Estestvoispytatelei (Travaux de la Société des Naturalistes de St.-Pétersbourg).</em> 12: 1-170; 13: 1-85, 4 pls., available online at https://play.google.com/books/reader?id=BXlBAQAAMAAJ&pg=GBS.PP6 [details]
additional source Hansen, H.J. (1908). Crustacea Malacostraca. I. <em>The Danish Ingolf-Expedition.</em> 3 (2): 1-120: pls. 1-5. [details]
additional source Holt, E.W.L.; Tattersall, W.M. (1905). Schizopodous Crustacea from the north-east Atlantic slope. In: Report on the Sea and Inland Fisheries of Ireland in 1902 and 1903. Part II. Scientific Investigations, pp. 99-152, pls 1-11. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Mauchline, J.; Murano, M. (1977). World list of the Mysidacea, Crustacea. <em>J. Tokyo Univ. Fish.</em> 64 (1): 39-88. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Sars, G.O. (1870). Carcinologiske Bidrag til Norges Fauna. I. <em>Monographi over de ved Norges Kyster forekommende Mysider. Pt. 1 Christiania, K. Norske Viidenskab. Trondhjem.</em> 64 pp., pls. I-V. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Sars, G. O. (1879). Carcinologiske Bidrag til Norges fauna. I. <em>Monographi over de ved Norges Kyster forekommende Mysider. Pt. 3. Christiania, A.W. Brøgger.</em> pp. 1-131, 42 pls. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Tattersall, O. S. (1955). Mysidacea. <em>Discovery Rep.</em> 28: 1-190. [details] Available for editors
additional source Tattersall, W. M. (1939). The Euphausiacea and Mysidacea of the John Murray Expedition to the Indian Ocean. <em>Sci. Rep. John Murray Exped.</em> 5: 203-246. [details] Available for editors
additional source Tattersall, W. M. (1951). A review of the Mysidacea of the United States National Museum. <em>Smithsonian Institution United States National Museum Bulletin.</em> 201: 1-292., available online at https://play.google.com/store/books/details?id=-vhMAAAAYAAJ&rdid=book--vhMAAAAYAAJ [details] Available for editors
additional source Stephensen, K. (1938). Euphausiacea, Mysidacea, Cumacea, and Nebaliacea. <em>In: Jensen, Ad. S., et al., (eds.), The zoology of Iceland. Copenhagen and Reykjavik, Levin & Munksgaard.</em> 3 (29): 1-24,1pl. [details] Available for editors
additional source Brattegard, T.; Meland K. (1997). Mysidacea (Crustacea) in the Faroe Area. <em>Frodskaparrit.</em> 45: 69-95. [details] Available for editors
additional source Price, W. (2001). Mysida Bibliography. <em>Internet.</em> [details] Available for editors
additional source Brattegard, T. & Vader, W. (1972). A collection of Peracarida from Möre and Romsdal, Northwestern Norway. <em>Sarsia.</em> 49(1): 33-40. [details] Available for editors
additional source BRANDT, A. (1997). Biodiversity of peracarid crustaceans (Malacostraca) from the shelf down to the deep arctic Ocean. <em>Biodiversity and conservation.</em> 6(11): 1533-1556. [details] Available for editors
additional source Wooldridge, T. H.; Mees, J. (2011 onwards). World List of the Mysidacea. [details]
additional source De Roa, E. Z.; Delgado, M. (1989). Pleurerythrops americana, a new species of mysidacea from the coast of Venezuela. <em>Sarsia.</em> 74(2): 91-93., available online at https://doi.org/10.1080/00364827.1989.10420526 [details] Available for editors
additional source Murano, M. (1981). Mysidacea from the central and western Pacific. 5. Genera Heteroerythrops, Meierythrops, Pleurerythrops, Gibberythrops, Illigiella, Dactylamblyops, Pseudamblyops, Paramblyops, Dactylerythrops and Nakazawai (tribe Erythropini). <em>Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory.</em> 26(4/6): 261-302. [details] Available for editors
additional source Murano, M. (1970). A small collection of benthic Mysidacea from coastal waters in Suruga Bay, Japan. <em>Crustaceana.</em> 18: 251-268. [details] Available for editors
additional source Panampunnayil, S.U. 1977. Three new species of Mysidacea from Kerala coast. Pages 28-35, In: Proceedings of the Symposium on Warm Water Zooplankton. National Institute of Oceanography, Goa, India. [details] Available for editors
additional source Panampunnayil, S.U. (1998). Descriptions of Indoerythrops typicus gen. Nov., sp. Nov. And Pleurerythrops inscita new record from Indian Waters (Crustacea: Mysidacea). <em>Journal of Plankton Research.</em> 20(4): 619-629. [details] Available for editors
additional source Wittmann, K.J. (2001). Centennial changes in the near-shore mysid fauna of the Gulf of Naples (Mediterranean Sea), with description of <i>Heteromysis riedli</i> sp. n. (Crustacea, Mysidacea). <em>Marine Ecology.</em> 22(1-2): 85-109. [details] Available for editors
additional source Illig, G. (1930). Die Schizopoden der deutschen Tiefsee-Expedition. <em>Rep. Valdivia Exped.</em> 22: 397-625. [details] Available for editors
additional source Neyt, K. (2002). Morfologische studie van een nieuwe soort van de ordo Mysidacea uit de Westelijke Indische Oceaan. Unpublished manuscript, Institute voor Dierkunde, Universiteit Gent, Mariene Biologie. [details] Available for editors
additional source Nouvel, H. (1949). Mysidacea. <em>In: Jespersen, P., & F.S. Russell (eds.), Fiches d´Identification du Zooplankton. Copenhagen. Conseil Permanent International pour l´Exploration de la Mer.</em> [details] Available for editors
additional source Stephensen, K. (1933). The Godthaab expedition 1928. Schizopoda. <em>Meddel. Grønland.</em> 79 (9): 1-20. [details] Available for editors
additional source Astthorson, O. S. (1984). The distribution and biology of mysids in Icelandic subarctic waters as demonstrated by analysis of cod stomach contents. <em>Sarsia.</em> 69 (2): 107-116. [details] Available for editors
additional source Astthorson, O. S. (1985). Mysids occuring in the stomachs of cod caught in the Atlantic water south and west of Iceland. <em>Sarsia.</em> 70 (2-3): 173-178. [details] Available for editors
additional source Bacescu, M. (1941). Les Mysidacés des eaux méditerranéennes de la France (spécialement de Banyuls) et des eaux de Monaco. <em>Bull. Inst. Océanogr.</em> 795: 1-46. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source COLOSI, G. (1929). I Misidacei del Golfo di Napoli. Pubbl. Staz. Zool. Napoli, 29: 405-441 [details] Available for editors
additional source COLOSI, G. (1930). Remarques sur la distribution horizontale et verticale des mysidés mediterranéens. - Bull. Soc. Océnogr. France, 10: 983-985 [details] Available for editors
additional source CUNHA, M.R. & JORBE J.C. & BERNARDES C. (1997). On the structure of the neretic suprabenthic communities from the Portugese continental margin Marine Ecology progress series 157: 119-137 [details] Available for editors
additional source ELIZALDE, M. & DAUVIN, J-C & SORBE J-C (1991). Las comunidades suprabentonicas batiales del golfa de Vizcaya (margen sur del canon de cap-ferret): composicion faunitica y estructura [details] Available for editors
additional source ELIZALDE, M. & DAUVIN, J-C & SORBE J-C (1991). Les Mysidacés suprabenthiques de la marge sud du Canyon du cap-ferret (Golfe de Gascogne): répartition bathymétrique et activité natatoire Ann. Inst. Océanogr. 67 (2): 129-144 [details] Available for editors
additional source ELIZALDE M.Répartition bathymétrique et activité natatoire près du fond des mysidacés suprabenthiques de la marge sud du canyon du cap-ferret (Golfe de Gascogne) [details] Available for editors
additional source Hansen, H.J. (1910). Revideret Fortegnelse over Danmarks marine Arter af Isopoda, Tanaidacea, Cumacea, Mysidacea og Euphausiacea. <em>Videnskabelige Meddelelser fra den Naturhistorisk Forening i København.</em> 1909: 197-289., available online at http://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/35855695 [details]
additional source HARGREAVES, P.M. (1985). The distribution of Mysidacea in the open ocean and Atlantic Ocean during 1979. - J. Plankton Res., 7 (2): 241-261. [ecology [details] Available for editors
additional source HOLT, E.W.L. & W.I. BEAUMONT (1900). Survey of fishing-grounds, west coast of Ireland, 1890-1891. X. Report on the Crustacea Schizopoda of Ireland. - Sci. Trans. r. Dublin Soc.,N.S., 7: 223692352,1pl [details]
additional source Lagardère, J.-P. (1985). Biogéographie et composition taxonomique du peuplement abyssal de Mysidacés. <i>In</i>: Laubier, L.; Monniot, Cl., (eds) Peuplement profonds du Golfe de Gascogne: 630 p,. [details] Available for editors
additional source MAUCHLINE, J. (1971). Seasonal occurence of mysids (Crustacea) and evidence of social behaviour. - J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K., 51: 809-825. [biology, ecology [details] Available for editors
additional source MURANO, M. (1970). Systematic and ecological studies on Mysidacea collected by the bottom-net. - J. oceanogr. Soc. Japan, 26: 137-150. [ecology [details] Available for editors
additional source Murano, M. (1977). Mysidacea from the Central and Western Pacific IV. Genera Euchaetomera, Euchaetomeropsis, Arachnomysis, Echinomysides, Meterythrops and Nipponerythrops (tribe Erythropini). <em>Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory.</em> 24 (1/3): 141-192. [details] Available for editors
additional source Pillai, N. K. (1965). A review of the work of shallow-water Mysidacea of the Indian waters. <em>Proc. Symposium Crust.</em> 5: 1681-1728. [details] Available for editors
additional source Ruiyu, L. & Shaowu, W. (1986). Studies of the Mysinae (Crustacea, Mysidacea) of the northern South China Sea. <em>Studia Marina Sinica.</em> 26: 159-202. [details] Available for editors
additional source STEPHENSEN, K. (1943). The zoology of East Greenland. Leptostraca, Mysidacea, Cumacea, Tanaidacea, Isopoda and Euphausiacea. - Medd. om Grønland, 121 (10): 1-82 [details] Available for editors
additional source TATTERSALL, O.S. (1957). Discovery reports issued by the national Institute of Oceanography Cambridge University press volume XXVII [details] Available for editors
additional source TATTERSALL, W.M. (1909). The Schizopoda collected by the "Maia" and "Puritan" in the Mediterranean. Mitt. zool. Stn. Neapel, 19: 117-143 [details]
additional source Zimmer, C,. (1914). Die Schizopoden der deutschen Südpolar-Expedition 1901-1903. In: von Drygalski (ed.), Deutsche Südpolar-Expedition 1901-1903,. 15, Zool., 7: 377-445. [details]
additional source Murano, M.; Krygier, E. (1985). Bathypelagic mysids from the northeastern Pacific. <em>J. Crust. Biol.</em> 5(4): 686-706. [details] Available for editors
additional source Hanamura, Y.; Kase, T. (2002). Marine cave mysids of the genus Palaumysis (Crustacea: Mysidacea), with a description of a new species from the Philippines. <em>Journal of Natural History.</em> 36: 253-263. (look up in IMIS), available online at https://doi.org/10.1080/00222930010004241 [details] Available for editors
 Present
Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio
Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
From editor or global species database
Depth range 28-240m [details]Habitat muddy sand, sandy mud [details]
Taxonomic remark Email from Karl Wittmann to Jan Mees dd 8-9-2015: Many species names of Erythropinae are badly spelled. In those cases where the genus name ends with "-ops" and the species name is an adjective, the name has to be transferred from female to male gender. [details]