WoRMS taxon details
Aurelia aurita (Linnaeus, 1758)
135306 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:135306)
accepted
Species
Aurellia flavidula Peron & Lesueur · unaccepted (synonym)
Medusa aurita Linnaeus, 1758 · unaccepted (basionym)
Medusa purpurea Pennant, 1777 · unaccepted
marine, fresh, terrestrial
(of Medusa aurita Linnaeus, 1758) Linnaeus, C. (1758). Systema Naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. <em>Editio decima, reformata [10th revised edition], vol. 1: 824 pp. Laurentius Salvius: Holmiae.</em> , available online at https://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/726886
page(s): 660 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
page(s): 660 [details] Available for editors
Neotype MZUSP 8657, geounit Helgoland
Neotype MZUSP 8657, geounit Helgoland [details]
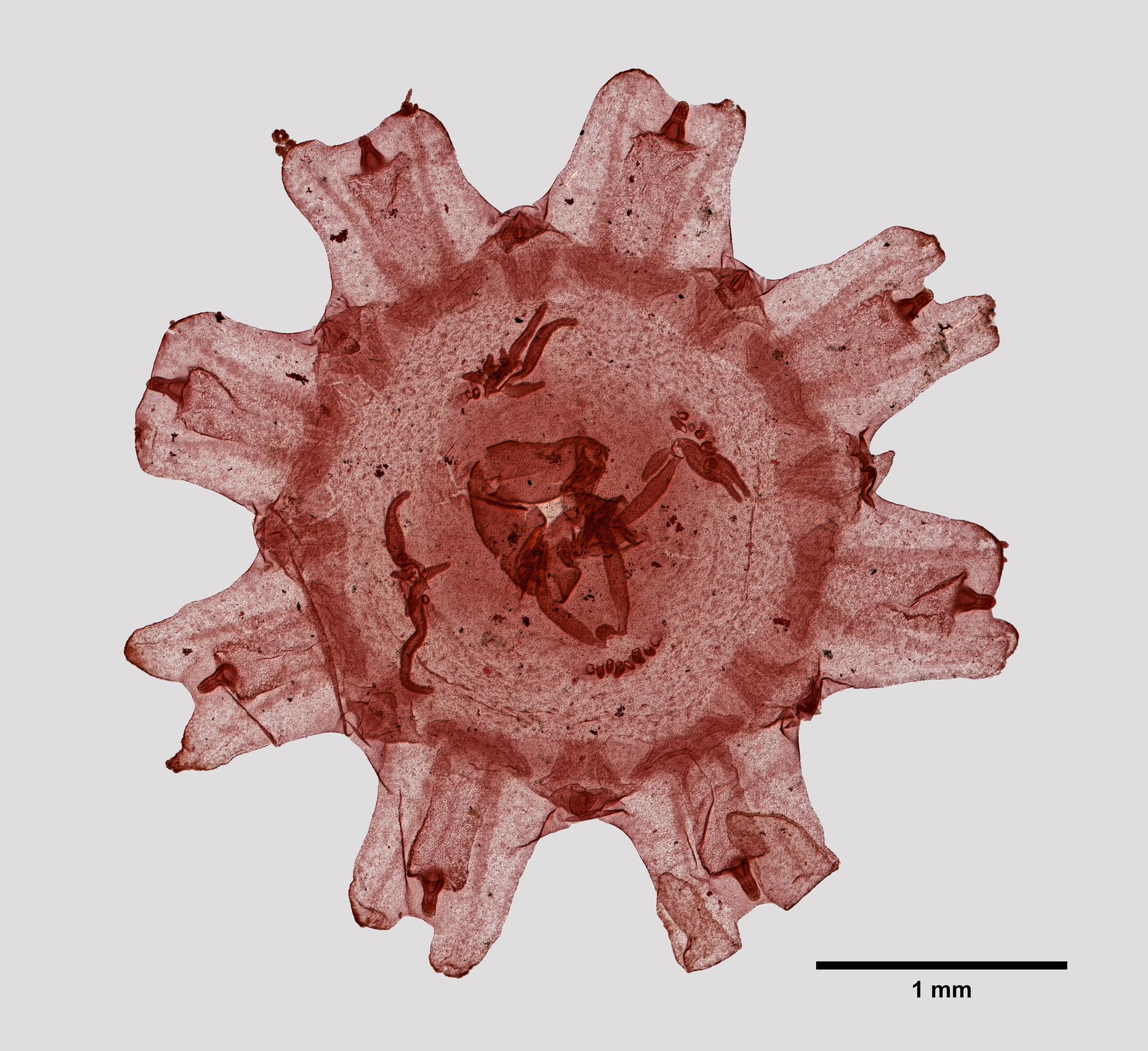
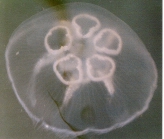
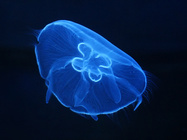
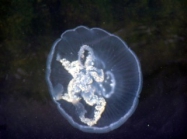
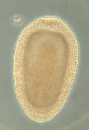
Description Width 15-30 cm. Bell flat to domed, firm, translucent, with four (or 5-7) bluish-pink gonad rings, four mouth-arms and...
Distribution Cosmopolitan species.
Description Width 15-30 cm. Bell flat to domed, firm, translucent, with four (or 5-7) bluish-pink gonad rings, four mouth-arms and hundreds of fine marginal tentacles. Swarms. Habitat: coastal. Distribution: all seas (Richmond, 1997). [details]
Distribution Cosmopolitan species.
Distribution Cosmopolitan species. [details]
Collins, A.G.; Morandini, A.C. (2024). World List of Scyphozoa. Aurelia aurita (Linnaeus, 1758). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=135306 on 2024-09-25
Date
action
by
![]() The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License
The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License
original description
(of Aurellia flavidula Peron & Lesueur) Péron F. & Lesueur C.A. (1810). Tableau des caractères génériques et spécifiques de toutes les espèces de méduses connues jusqu'à ce jour. <em>Annales du Muséum national d'histoire naturelle de Paris.</em> 14: 325-366., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/3498981
page(s): 359 [details]
original description (of Medusa aurita Linnaeus, 1758) Linnaeus, C. (1758). Systema Naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. <em>Editio decima, reformata [10th revised edition], vol. 1: 824 pp. Laurentius Salvius: Holmiae.</em> , available online at https://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/726886
page(s): 660 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
original description (of Medusa purpurea Pennant, 1777) Pennant, T. (1777). British Zoology, vol. IV. Crustacea. Mollusca. Testacea. <em>London.</em> i-viii, 1-154, pls. 1-93., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/127011
page(s): 57 [details]
context source (Deepsea) Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) of UNESCO. The Ocean Biogeographic Information System (OBIS), available online at http://www.iobis.org/ [details]
context source (HKRMS) Morton, B. & Morton, J. (1983). <i>The sea shore ecology of Hong Kong</i>. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press. 350 pp. [details]
context source (Schelde) Dankwa, H. R. (1993). Utilization of estuarine salt marshes by postlarval brown shrimp Crangon crangon. <em>MSc Thesis. RUG: Gent.</em> 49 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details]
context source (BeRMS 2020) Marine Biology Section, Ugent. Belgium. INRAM. Benthic fauna monitoring- SSD - Belgian Science Policy., available online at http://www.vliz.be/projects/inram/imers.php. [details]
context source (Bermuda) Bigelow, H. B. (1938). Plankton of the Bermuda Oceanographic Expeditions VIII. Medusae taken during the years 1929 and 1930. Zoologica (New York), 23(5): 99-189 [details]
context source (Hexacorallia) Fautin, Daphne G. (2013). Hexacorallians of the World. (look up in IMIS) [details]
basis of record Cornelius, P.F.S. (2001). Cubozoa, <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 111 (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Gosner, K. L. (1971). Guide to identification of marine and estuarine invertebrates: Cape Hatteras to the Bay of Fundy. <em>John Wiley & Sons, Inc., London.</em> 693 pp. [pdf copepod and branchiuran :445-455]. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Larson, R.J. 1976. Marine flora and fauna of the northeastern United States. Cnidaria: Scyphozoa. NOAA Techical Report NMFS Circular 397. 18 p. [details]
additional source Linkletter, L. E. (1977). A checklist of marine fauna and flora of the Bay of Fundy. <em>Huntsman Marine Laboratory, St. Andrews, N.B.</em> 68: p. [details]
additional source Meinkoth, N. A. (1981). Field guide to North American seashore creatures. <em>The Audubon Society.</em> 1-799. [details]
additional source Thomas, M. L. H. (1983). Marine and coastal systems of the Quoddy Region, New Brunswick. <em>Canadian Special Publication of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences.</em> 64:1-306. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Richmond, M. (Ed.) (1997). A guide to the seashores of Eastern Africa and the Western Indian Ocean islands. Sida/Department for Research Cooperation, SAREC: Stockholm, Sweden. ISBN 91-630-4594-X. 448 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Muller, Y. (2004). Faune et flore du littoral du Nord, du Pas-de-Calais et de la Belgique: inventaire. [Coastal fauna and flora of the Nord, Pas-de-Calais and Belgium: inventory]. <em>Commission Régionale de Biologie Région Nord Pas-de-Calais: France.</em> 307 pp., available online at http://www.vliz.be/imisdocs/publications/145561.pdf [details]
additional source Shih, C.T., 1977. A guide to the Jellyfish of Canadian Atlantic waters. National Museum of Natural Sciences, Natural History Series 5 : 1-190. [details]
additional source Haeckel, E. (1880). Das System der Acraspeden. 2te Hälfte des Systems der Medusen. Acht Nachträge zur Vervollständigung des Systems. <em>Denkschriften der Medicinisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Gesellschaft zu Jena.</em> 2: 361-672, plates 21-40., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/32605982
page(s): 542, 544, 547, 552, 553, 554, 555, 556 [details]
additional source Vanderperren, J.-P. (1991). Report Natural History Archive 1990 [Verslag Natuurhistorisch Archief 1990]. <em>De Strandvlo.</em> 11(3): 65-75. (look up in IMIS)
page(s): 67 [details]
additional source Segura-Puertas, L., L. Celis, and L. Chiaverano. 2009. Medusozoans (Cnidaria: Cubozoa, Scyphozoa, and Hydrozoa) of the Gulf of Mexico, Pp. 369–379 in Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. Biodiversity. Texas A&M Pre [details]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Cairns, S.D., L. Gershwin, F.J. Brook, P. Pugh, E.W. Dawson, O.V.; Ocaña, W. Vervoort, G. Williams, J.E. Watson, D.M. Opresko, P. Schuchert, P.M. Hine, D.P. Gordon, H.I. Campbell, A.J. Wright, J.A.Sánchez & D.G. Fautin. (2009). Phylum Cnidaria: corals, medusae, hydroids, myxozoans. <em>in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2009). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 1. Kingdom Animalia: Radiata, Lophotrochozoa, Deuterostomia.</em> pp. 59-101., available online at https://repository.si.edu/handle/10088/8431 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Trott, T. J. (2004). Cobscook Bay inventory: a historical checklist of marine invertebrates spanning 162 years. <em>Northeastern Naturalist.</em> 11, 261-324., available online at http://www.gulfofmaine.org/kb/files/9793/TROTT-Cobscook%20List.pdf [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). , available online at http://www.itis.gov [details]
additional source Howson, C.M. & B.E. Picton. (1997). The species directory of the marine fauna and flora of the British Isles and surrounding seas. <em>Ulster Museum Publication, 276. The Ulster Museum: Belfast, UK. ISBN 0-948150-06-8.</em> vi, 508 (+ cd-rom) pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
new combination reference Lamarck, J.-B. M. de. (1816). Histoire naturelle des animaux sans vertèbres. Tome second. <em>Paris. Verdière.</em> Vol. 2 pp. 1-568., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/47698
page(s): 513 [details]
page(s): 359 [details]
original description (of Medusa aurita Linnaeus, 1758) Linnaeus, C. (1758). Systema Naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. <em>Editio decima, reformata [10th revised edition], vol. 1: 824 pp. Laurentius Salvius: Holmiae.</em> , available online at https://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/726886
page(s): 660 [details] Available for editors
original description (of Medusa purpurea Pennant, 1777) Pennant, T. (1777). British Zoology, vol. IV. Crustacea. Mollusca. Testacea. <em>London.</em> i-viii, 1-154, pls. 1-93., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/127011
page(s): 57 [details]
context source (Deepsea) Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) of UNESCO. The Ocean Biogeographic Information System (OBIS), available online at http://www.iobis.org/ [details]
context source (HKRMS) Morton, B. & Morton, J. (1983). <i>The sea shore ecology of Hong Kong</i>. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press. 350 pp. [details]
context source (Schelde) Dankwa, H. R. (1993). Utilization of estuarine salt marshes by postlarval brown shrimp Crangon crangon. <em>MSc Thesis. RUG: Gent.</em> 49 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details]
context source (BeRMS 2020) Marine Biology Section, Ugent. Belgium. INRAM. Benthic fauna monitoring- SSD - Belgian Science Policy., available online at http://www.vliz.be/projects/inram/imers.php. [details]
context source (Bermuda) Bigelow, H. B. (1938). Plankton of the Bermuda Oceanographic Expeditions VIII. Medusae taken during the years 1929 and 1930. Zoologica (New York), 23(5): 99-189 [details]
context source (Hexacorallia) Fautin, Daphne G. (2013). Hexacorallians of the World. (look up in IMIS) [details]
basis of record Cornelius, P.F.S. (2001). Cubozoa, <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 111 (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Gosner, K. L. (1971). Guide to identification of marine and estuarine invertebrates: Cape Hatteras to the Bay of Fundy. <em>John Wiley & Sons, Inc., London.</em> 693 pp. [pdf copepod and branchiuran :445-455]. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Larson, R.J. 1976. Marine flora and fauna of the northeastern United States. Cnidaria: Scyphozoa. NOAA Techical Report NMFS Circular 397. 18 p. [details]
additional source Linkletter, L. E. (1977). A checklist of marine fauna and flora of the Bay of Fundy. <em>Huntsman Marine Laboratory, St. Andrews, N.B.</em> 68: p. [details]
additional source Meinkoth, N. A. (1981). Field guide to North American seashore creatures. <em>The Audubon Society.</em> 1-799. [details]
additional source Thomas, M. L. H. (1983). Marine and coastal systems of the Quoddy Region, New Brunswick. <em>Canadian Special Publication of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences.</em> 64:1-306. [details] Available for editors
additional source Richmond, M. (Ed.) (1997). A guide to the seashores of Eastern Africa and the Western Indian Ocean islands. Sida/Department for Research Cooperation, SAREC: Stockholm, Sweden. ISBN 91-630-4594-X. 448 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Muller, Y. (2004). Faune et flore du littoral du Nord, du Pas-de-Calais et de la Belgique: inventaire. [Coastal fauna and flora of the Nord, Pas-de-Calais and Belgium: inventory]. <em>Commission Régionale de Biologie Région Nord Pas-de-Calais: France.</em> 307 pp., available online at http://www.vliz.be/imisdocs/publications/145561.pdf [details]
additional source Shih, C.T., 1977. A guide to the Jellyfish of Canadian Atlantic waters. National Museum of Natural Sciences, Natural History Series 5 : 1-190. [details]
additional source Haeckel, E. (1880). Das System der Acraspeden. 2te Hälfte des Systems der Medusen. Acht Nachträge zur Vervollständigung des Systems. <em>Denkschriften der Medicinisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Gesellschaft zu Jena.</em> 2: 361-672, plates 21-40., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/32605982
page(s): 542, 544, 547, 552, 553, 554, 555, 556 [details]
additional source Vanderperren, J.-P. (1991). Report Natural History Archive 1990 [Verslag Natuurhistorisch Archief 1990]. <em>De Strandvlo.</em> 11(3): 65-75. (look up in IMIS)
page(s): 67 [details]
additional source Segura-Puertas, L., L. Celis, and L. Chiaverano. 2009. Medusozoans (Cnidaria: Cubozoa, Scyphozoa, and Hydrozoa) of the Gulf of Mexico, Pp. 369–379 in Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. Biodiversity. Texas A&M Pre [details]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Cairns, S.D., L. Gershwin, F.J. Brook, P. Pugh, E.W. Dawson, O.V.; Ocaña, W. Vervoort, G. Williams, J.E. Watson, D.M. Opresko, P. Schuchert, P.M. Hine, D.P. Gordon, H.I. Campbell, A.J. Wright, J.A.Sánchez & D.G. Fautin. (2009). Phylum Cnidaria: corals, medusae, hydroids, myxozoans. <em>in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2009). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 1. Kingdom Animalia: Radiata, Lophotrochozoa, Deuterostomia.</em> pp. 59-101., available online at https://repository.si.edu/handle/10088/8431 [details] Available for editors
additional source Trott, T. J. (2004). Cobscook Bay inventory: a historical checklist of marine invertebrates spanning 162 years. <em>Northeastern Naturalist.</em> 11, 261-324., available online at http://www.gulfofmaine.org/kb/files/9793/TROTT-Cobscook%20List.pdf [details] Available for editors
additional source Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). , available online at http://www.itis.gov [details]
additional source Howson, C.M. & B.E. Picton. (1997). The species directory of the marine fauna and flora of the British Isles and surrounding seas. <em>Ulster Museum Publication, 276. The Ulster Museum: Belfast, UK. ISBN 0-948150-06-8.</em> vi, 508 (+ cd-rom) pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
new combination reference Lamarck, J.-B. M. de. (1816). Histoire naturelle des animaux sans vertèbres. Tome second. <em>Paris. Verdière.</em> Vol. 2 pp. 1-568., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/47698
page(s): 513 [details]
 Present
Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio
Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
Neotype MZUSP 8657, geounit Helgoland [details]
From editor or global species database
Synonymy Aurelia BOR lineage Schroth et al., 2002.Aurelia borealis Schroth et al., 2002. [details]
Unverified
Description Width 15-30 cm. Bell flat to domed, firm, translucent, with four (or 5-7) bluish-pink gonad rings, four mouth-arms and hundreds of fine marginal tentacles. Swarms. Habitat: coastal. Distribution: all seas (Richmond, 1997). [details]Distribution Cosmopolitan species. [details]
Habitat coastal [details]
Habitat upper epipelagic [details]
Remark In Belgium, the media always correlates Aurelia-invasions to excellent weather conditions in summer. Instead, the occurrence or absence of Aurelia is correlated to winter conditions. Seawater temperatures are within the limits for strobulation (4° to 10°C) from December to April. Since 1987 till 2003 there were no records of medusa of Aurelia aurita in Belgium in the years 1994, 1995, 2000 and 2002. In these years seawater temperatures were higher than 6C in February. Polyps strobulate and the ephyra grow during the following three months till adolescent proportions. These medusa are beached in late spring and early summer, when tourists are common on our beaches.
Abnormalities in the number of gonads are as frequent as in the beginning of the last century (Russell, 1970). Out of 1988 specimens, 39 specimen or 1.96% had five, six or seven gonads instead of four. [details]
| Language | Name | |
|---|---|---|
| Albanian | meduza hënë | [details] |
| Catalan | borm | [details] |
| Danish | vandmand | [details] |
| Dutch | oorkwalgeoorde zeekwal | [details] |
| English | moon jellyfishmoon jellycommon jellyfish | [details] |
| Finnish | korvameduusa | [details] |
| French | méduse luneméduse communeméduse bleueaurélie | [details] |
| German | Ohrenqualle | [details] |
| Italian | pota marinamedusa quadrifoglio | [details] |
| Japanese | ミズクラゲ | [details] |
| Norwegian | glasmanet | [details] |
| Polish | chełbia modra | [details] |
| Portuguese | medusa-da-lua | [details] |
| Russian | Аурелия ушастая | [details] |
| Spanish | medusa sombrillamedusa platillomedusa lunamedusa común | [details] |
| Swedish | öronmanet | [details] |
| Turkish | ay denizanas | [details] |
Marine Life Information Network - UK
PlanktonNet Image
To Barcode of Life (245 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (180 publications) (from synonym Aurellia flavidula Peron & Lesueur)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (721 publications)
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL)
To Digital Atlas Of Marine Species & Locations, DAMSL (Moon Jellyfish)
To Dyntaxa
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Aurelia aurita)
To Fishipedia
To GenBank (255502 nucleotides; 480 proteins)
To GenBank (255502 nucleotides; 480 proteins) (from synonym Medusa aurita Linnaeus, 1758)
To Global Biotic Interactions (GloBI)
To PESI
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (99 records)
To Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History (YPM IZ 095705)
To ITIS
PlanktonNet Image
To Barcode of Life (245 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (180 publications) (from synonym Aurellia flavidula Peron & Lesueur)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (721 publications)
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL)
To Digital Atlas Of Marine Species & Locations, DAMSL (Moon Jellyfish)
To Dyntaxa
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Aurelia aurita)
To Fishipedia
To GenBank (255502 nucleotides; 480 proteins)
To GenBank (255502 nucleotides; 480 proteins) (from synonym Medusa aurita Linnaeus, 1758)
To Global Biotic Interactions (GloBI)
To PESI
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (99 records)
To Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History (YPM IZ 095705)
To ITIS