WoRMS taxon details
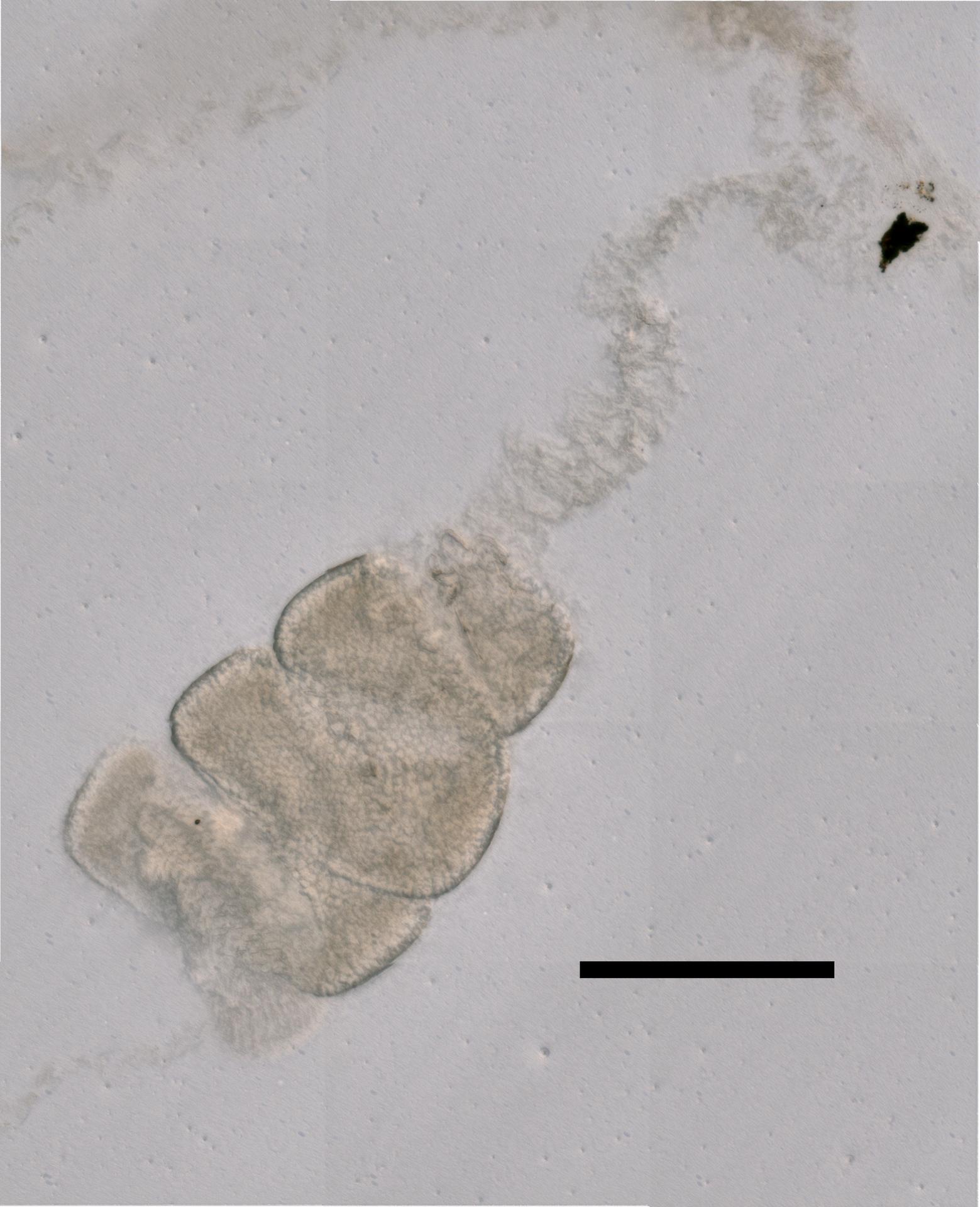
Nanomia cara Agassiz, 1865
135496 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:135496)
accepted
Species
Cupulita cara (A. Agassiz, 1865) · unaccepted (Unaccepted combination)
Stephanomia cara (A. Agassiz, 1865) · unaccepted
marine, brackish, fresh, terrestrial
recent only
Agassiz, A. 1865a. Nanomia cara. - Proceedings of the Boston Society of Natural History 9: 181., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/32011192
page(s): 181 [details]
page(s): 181 [details]
Distribution semi-cosmopolitan, mainly temperate
Distribution semi-cosmopolitan, mainly temperate [details]
Schuchert, P.; Choong, H.; Galea, H.; Hoeksema, B.; Lindsay, D.; Manko, M.; Pica, D. (2025). World Hydrozoa Database. Nanomia cara Agassiz, 1865. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=135496 on 2025-05-27
Date
action
by
![]() The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 License
The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 License
Nomenclature
original description
Agassiz, A. 1865a. Nanomia cara. - Proceedings of the Boston Society of Natural History 9: 181., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/32011192
page(s): 181 [details]
page(s): 181 [details]
Taxonomy
redescription
Agassiz, A. (1865). North American Acalephae. <em>Illustrated Catalogue of the Museum of Comparative Zoölogy at Harvard College.</em> 2: 1-234., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/bibliography/1837
page(s): 200, figs 331-350 [details]
status source Hosia A., Martell L., Manko M.K., Haddock S.H.D., Haberlin D., Mapstone G.M. (2024). Unexpected diversity and novel lineages in the cosmopolitan genus Nanomia (Cnidaria: Siphonophorae: Physonectae). <em>Frontiers in Marine Science.</em> 11:1421514., available online at https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2024.1421514
page(s): 10, figs 7-9; note: molecular analysis [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
page(s): 200, figs 331-350 [details]
status source Hosia A., Martell L., Manko M.K., Haddock S.H.D., Haberlin D., Mapstone G.M. (2024). Unexpected diversity and novel lineages in the cosmopolitan genus Nanomia (Cnidaria: Siphonophorae: Physonectae). <em>Frontiers in Marine Science.</em> 11:1421514., available online at https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2024.1421514
page(s): 10, figs 7-9; note: molecular analysis [details] Available for editors
Ecology
ecology source
Fewkes, J.W., 1888. On certain medusae from New England. In: Studies from the Newport marine zool. Lab. Bull. Mus. comp. Zool. Harv. 13 7: 209-240., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/3897617 [details]
Other
context source (Deepsea)
Pugh, P. R. (2013). Confirmed records of Siphonophorae found below 500 m depth. (personal database). [details]
additional source Fewkes, J.W., 1888. On certain medusae from New England. In: Studies from the Newport marine zool. Lab. Bull. Mus. comp. Zool. Harv. 13 7: 209-240., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/3897617
page(s): 213, pls 1-3 [details]
additional source Trott, T. J. (2004). Cobscook Bay inventory: a historical checklist of marine invertebrates spanning 162 years. <em>Northeastern Naturalist.</em> 11, 261-324., available online at http://www.gulfofmaine.org/kb/files/9793/TROTT-Cobscook%20List.pdf [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). , available online at http://www.itis.gov [details]
additional source Brunel, P., L. Bosse & G. Lamarche. (1998). Catalogue of the marine invertebrates of the estuary and Gulf of St. Lawrence. <em>Canadian Special Publication of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 126.</em> 405 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Totton, A. K. 1965. A Synopsis of the Siphonophora. London, British Museum (Natural History). Pp. 230.
page(s): 72, fig.37 [details]
additional source Kramp, P. L. (1942). Siphonophora. The Godthaab Expedition 1928. <em>Medd. Grønl.</em> 80 (8): 3-24.
page(s): 13 [details]
additional source Rossi, S., M.J. Youngbluth, C.A. Jacoby, F. Pagès & X. Garrofé. (2008). Fatty acid trophic markers and trophic links among seston, crustacean zooplankton and the siphonophore Nanomia cara in Georges Basin and Oceanographer Canyon (NW Atlantic). Scientia Marina 72(2):403-416.
page(s): 403-416, fig.2 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Hosia, A., & Bamstedt, U. 2008. Seasonal abundance and vertical distribution of siphonophores in western Norwegian fjords. Journal of Plankton Research 30: 951-962., available online at https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbn045
page(s): 951 [details]
additional source Baxter, E.J., R. McAllen, A.L. Allcock & T.K. Doyle. (2012). Abundance, distribution and community composition of small gelatinous zooplankton in southern irish coastal waters. Biology & Environment 112B(1):91-103., available online at http://www.doi.org/10.3318/b1oe.2012.01 [details]
additional source Fewkes, J.W., 1888. On certain medusae from New England. In: Studies from the Newport marine zool. Lab. Bull. Mus. comp. Zool. Harv. 13 7: 209-240., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/3897617
page(s): 213, pls 1-3 [details]
additional source Trott, T. J. (2004). Cobscook Bay inventory: a historical checklist of marine invertebrates spanning 162 years. <em>Northeastern Naturalist.</em> 11, 261-324., available online at http://www.gulfofmaine.org/kb/files/9793/TROTT-Cobscook%20List.pdf [details] Available for editors
additional source Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). , available online at http://www.itis.gov [details]
additional source Brunel, P., L. Bosse & G. Lamarche. (1998). Catalogue of the marine invertebrates of the estuary and Gulf of St. Lawrence. <em>Canadian Special Publication of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 126.</em> 405 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Totton, A. K. 1965. A Synopsis of the Siphonophora. London, British Museum (Natural History). Pp. 230.
page(s): 72, fig.37 [details]
additional source Kramp, P. L. (1942). Siphonophora. The Godthaab Expedition 1928. <em>Medd. Grønl.</em> 80 (8): 3-24.
page(s): 13 [details]
additional source Rossi, S., M.J. Youngbluth, C.A. Jacoby, F. Pagès & X. Garrofé. (2008). Fatty acid trophic markers and trophic links among seston, crustacean zooplankton and the siphonophore Nanomia cara in Georges Basin and Oceanographer Canyon (NW Atlantic). Scientia Marina 72(2):403-416.
page(s): 403-416, fig.2 [details] Available for editors
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Hosia, A., & Bamstedt, U. 2008. Seasonal abundance and vertical distribution of siphonophores in western Norwegian fjords. Journal of Plankton Research 30: 951-962., available online at https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbn045
page(s): 951 [details]
additional source Baxter, E.J., R. McAllen, A.L. Allcock & T.K. Doyle. (2012). Abundance, distribution and community composition of small gelatinous zooplankton in southern irish coastal waters. Biology & Environment 112B(1):91-103., available online at http://www.doi.org/10.3318/b1oe.2012.01 [details]
 Present
Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio
Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
Unreviewed
Distribution semi-cosmopolitan, mainly temperate [details]Habitat epipelagic [details]
Habitat upper epipelagic and glacial [details]
| Language | Name | |
|---|---|---|
| Japanese | ナガヨウラクラゲ | [details] |
To Barcode of Life (20 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (65 publications)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (8 publications) (from synonym Stephanomia cara (A. Agassiz, 1865))
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL)
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Nanomia cara)
To GenBank (7 nucleotides; 7 proteins)
To PESI
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (21 records) (from synonym Stephanomia cara (A. Agassiz, 1865))
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (8 records)
To Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History (YPM IZ 106584)
To ITIS
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (65 publications)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (8 publications) (from synonym Stephanomia cara (A. Agassiz, 1865))
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL)
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Nanomia cara)
To GenBank (7 nucleotides; 7 proteins)
To PESI
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (21 records) (from synonym Stephanomia cara (A. Agassiz, 1865))
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (8 records)
To Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History (YPM IZ 106584)
To ITIS