|
 |
|
|
||
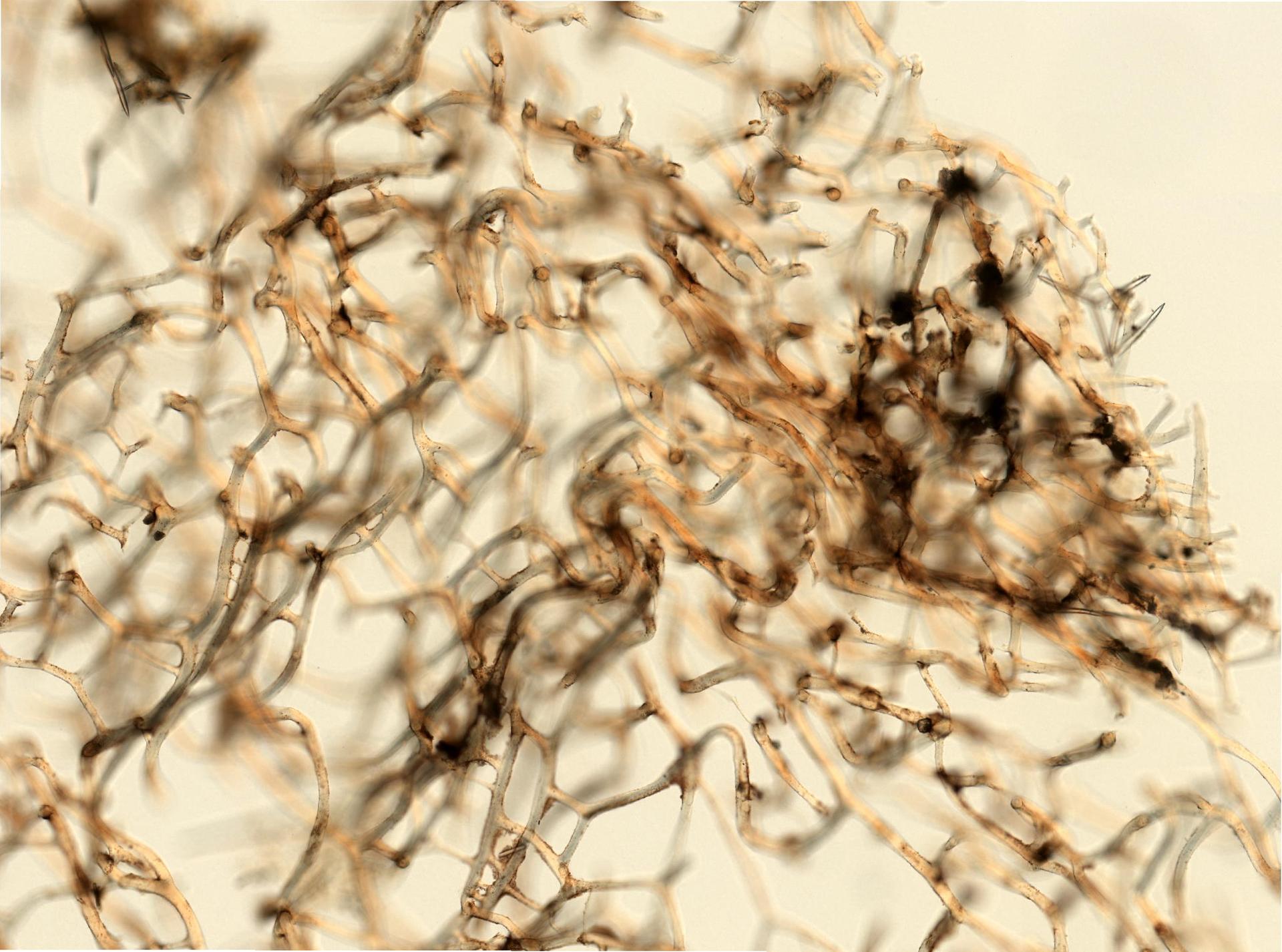
WoRMS name detailsSpongia officinalis Linnaeus, 1759
132407 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:132407)
alternative representation (subgenus assignment)
Species
marine,
recent only
Linnaeus, C. (1759). Systema naturæ per regna tria naturæ, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Tomus II. Editio decima, reformata. - pp. [1-4], 825-1384. Holmiæ. (L. Salvii)., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/587267
page(s): 1348 [details]
Neotype BMNH 1883.12.4.28
Neotype BMNH 1883.12.4.28 [details]
de Voogd, N.J.; Alvarez, B.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Cárdenas, P.; Díaz, M.-C.; Dohrmann, M.; Downey, R.; Goodwin, C.; Hajdu, E.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Kelly, M.; Klautau, M.; Lim, S.C.; Manconi, R.; Morrow, C.; Pinheiro, U.; Pisera, A.B.; Ríos, P.; Rützler, K.; Schönberg, C.; Turner, T.; Vacelet, J.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Xavier, J. (2024). World Porifera Database. Spongia officinalis Linnaeus, 1759. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=132407 on 2024-09-26
Date action by
original description
Linnaeus, C. (1759). Systema naturæ per regna tria naturæ, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Tomus II. Editio decima, reformata. - pp. [1-4], 825-1384. Holmiæ. (L. Salvii)., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/587267
page(s): 1348 [details] basis of record Cook, S. de C.; Bergquist, P.R. (2002). Family Spongiidae Gray, 1867. Pp. 1051-1060. <i>In</i>: Hooper, J.N.A. & Van Soest, R.W.M. (eds) <i>Systema Porifera - A guide to the classification of sponges</i>. (2 volumes) Kluwer Academic/ Plenum Publishers: New York, 1708 + xvliii. ISBN 0-306-47260-0 (printed version). [details] Available for editors basis of record Cook, S. de C.; Bergquist, P.R. (2002 [2004]]). Family Spongiidae Gray, 1867. Pp. 1051-1060. <i>In</i>: Hooper, J.N.A. & Van Soest, R.W.M. (eds) <i>Systema Porifera - A guide to the classification of sponges</i>. (2 volumes) Kluwer Academic/ Plenum Publishers, New York, 1708 + xvliii. ISBN 978-1-4615-0747-5 (eBook electronic version). [details] Available for editors additional source Pansini, M.; Musso, B. (1991). Sponges from trawl-exploitable bottoms of the Ligurian and Tyrrhenian Seas: distribution and ecology. <em>P.S.Z.N.I.: Marine Ecology.</em> 12 (4): 317-329. page(s): 321 [details] Available for editors additional source Berthet, B.; Mouneyrac, C.; Pérez, T.; Amiard-Triquet, C. (2005). Metallothionein concentration in sponges (<i>Spongia officinalis</i>) as a biomarker of metal contamination. <em>Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Part C.</em> 141(3): 306-313., available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2005.07.008 [details] Available for editors additional source Linnaeus, C. (1767). Systema naturae per regna tria naturae: secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Ed. 12. 1., Regnum Animale. 1 & 2. <em>Holmiae [Stockholm], Laurentii Salvii.</em> pp. 1-532 [1766] pp. 533-1327 [1767]., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/83650#5 page(s): 1298 [details] additional source Van Soest, R.W.M. (2001). Porifera, <b><i>in</i></b>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification</i>. <em>Collection Patrimoines Naturels.</em> 50: 85-103. (look up in IMIS) [details] additional source Bergquist, P.R. (1965). The Sponges of Micronesia, Part I. The Palau Archipelago. <em>Pacific Science.</em> 19 (2): 123-204. page(s): 127; note: Misapplication [details] Available for editors additional source Boury-Esnault, N. (1971). Spongiaires de la zone rocheuse de Banyuls-sur-Mer. II. Systématique. <em>Vie et Milieu.</em> 22(2): 287-349. page(s): 338-339; note: with a short description [details] Available for editors additional source Vacelet, J.; Verdenal, B.; Périnet, G. (1988). The iron mineralization of <i>Spongia officinalis</i> L. (Porifera, Dictyoceratida) and its relationships with the collagen skeleton. <em>Biology of the Cell.</em> 62: 189-198., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1768-322x.1988.tb00721.x page(s): 190 [details] Available for editors additional source Hussein, K.B.; Talet, L.B. (2019). A preliminary inventory of biodiversity and benthic habitats of “Plane” Island (Paloma) in Oran Bay, north western Algeria, (western Mediterranean). <em>Journal of the Black Sea / Mediterranean Environment.</em> 25 (1): 49-72. page(s): 59 [details] Available for editors additional source Bosc, L.A.G. (1802). Histoire Naturelle des Vers : contenant leur description et leurs moeurs, avec figures dessinées d'après nature. <em>Guilleminet, Paris, chez Deterville.</em> 3 vols. 324 pp. + pls. 1-10; 300 pp. + pls. 11-25; 270 pp. + pls. 26-32. 1-324., available online at http://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/41758184 page(s): 142 [details] additional source Agne, S.; Ekins, M.; Galitz, A.; Hofreiter, M.; Preick, M.; Straube, N.; Wörheide, G.; Erpenbeck, D. (2022). Keratose sponge MuseOMICS: setting reference points in dictyoceratid demosponge phylogeny. <em>Zootaxa.</em> 5195(3): 296-300., available online at https://www.mapress.com/zt/article/view/zootaxa.5195.3.9 page(s): 297 and 298 [details] Available for editors additional source Corriero, G. (1989). The sponge fauna from the Stagnone di Marsala (Sicily): taxonomic and ecological observations. <em>Bolletino Museo Istituto Biologia Università Genova.</em> 53: 101-113. page(s): 103 [details] additional source Rao, H.S. 1941. Indian and Ceylon sponges of the Naturhistoriska Riksmuseet, Stockholm collected by K. Fristedt. Records of the Indian Museum 43: 417-469. page(s): 454; note: Misapplication [details] additional source Müller, O.F. (1776). Zoologiae Danicae prodromus, seu Animalium Daniae et Norvegiae indigenarum: characteres, nomina, et synonyma imprimis popularium. <em>Typis Hallagerii, Havni, Copenhagen.</em> 282 pp., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/47550 page(s): 256; note: Misapplication for Spongionella pulchella. [details] additional source Ben Mustapha, K; Zarrouk, S.; Souissi, A.; El Abed, A. (2003). Diversité des Démosponges Tunisiennes. <em>Bulletin Institut national des Sciences et Technologies de la mer de Salammbô.</em> 30, 55-78. page(s): 73 [details] Available for editors additional source Carballo, J.L.; Garcia-Gómez, J.C. (1994). Esponjas del Estrecho de Gibraltar y áreas próximas, con nuevas aportaciones para la fauna Iberica [Porifera from the Straits of Gibraltar and nearby areas, new species of the Iberian fauna]. <em>Cahiers de Biologie Marine.</em> 35(2): 193-211. (look up in IMIS) page(s): 196 [details] additional source Lombas, I. (1982). Distribución, de esponjas esciafilas en la zona intermareal de Aramar (Luanco, Asturias). <em>Boletim de Ciencias Naturales IDEA.</em> 29: 37-50. page(s): 46 [details] Available for editors additional source Wilkens, C.F. (1787). P.S. Pallas, Charakteristik der Thierpflanzen. Nach seinem Tode herausgegeben von J.F.W. Herbst. <em>Raspischen Buchhandlung, Nürnberg.</em> pp. 265 + 22 (unnumbered) + pls. XXVI. page(s): 225 [details] additional source Olivi, G. (1792). Zoologia Adriatica, ossia catalogo ragionato degli animali del golfo e della lagune di Venezia. Bassano [G. Remondini e fl.]. [ix] + 334 + xxxii pp., 9 pls., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/123881 page(s): 262 [details] additional source Sarà, M. (1958). Contributo all consoscenza dei Poriferi del Mar Ligure. <em>Annali di Museo Civico di Storia Naturale Genova.</em> 70(1): 207-244. page(s): 239; pl XI [details] Available for editors additional source Pallas, P. S. (1766). Elenchus zoophytorum sistens generum adumbrationes generaliores et specierum cognitarum succintas descriptiones, cum selectis auctorum synonymis. <em>[book].</em> pp. 451, Fransiscum Varrentrapp, Hagae., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/6019361 page(s): 387 [details] additional source Burton, M. (1932). Sponges. <em>Discovery Reports.</em> 6: 237-392, pls 48-57. page(s): 340; note: misapplication [details] Available for editors additional source Burton, M. (1959). Sponges. <em>In: Scientific Reports. John Murray Expedition 1933-34. 10(5). British Museum (Natural History): London.</em> Pp. 151-281., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/49512735 page(s): 270; note: Misapplication [details] additional source Carter, H.J. (1876). Descriptions and Figures of Deep-Sea Sponges and their Spicules, from the Atlantic Ocean, dredged up on board H.M.S.‘Porcupine', chiefly in 1869 (concluded). <em>Annals and Magazine of Natural History.</em> (4) 18(105): 226-240; (106): 307-324; (107): 388-410;(108): 458-479, pls XII-XVI. page(s): 231-232; note: Misapplication [details] additional source Ellis, J.; Solander, D. (1786). The Natural History of many curious and uncommon Zoophytes, collected from various parts of the Globe. Systematically arranged and described by the late Daniel Solander. 4.(Benjamin White & Son: London): 1-206, pls 1-63., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/41943909 page(s): 183-184 [details] additional source Laubenfels, M.W. de. (1948). The order Keratosa of the phylum Porifera. A monographic study. <em>Occasional Papers of the Allan Hancock Foundation.</em> 3: 1-217. page(s): 4 [details] Available for editors additional source Lévi, C. (1957). Spongiaires des côtes d'Israel. <em>Bulletin of the Research Council of Israel.</em> 6 B(3-4): 201-212. page(s): 202 [details] Available for editors additional source Lévi, C. (1961). Spongiaires des Iles Philippines, principalement récoltées au voisinage de Zamboanga. <em>Philippine Journal of Science.</em> 88 (4): 509-533. page(s): 529; note: Misapplication [details] additional source Poiret, J.-L. M. (1789). Voyage en Barbarie, ou Lettres écrites de l'Ancienne Numidie pendant les Années 1785 et 1786, avec un Essai sur l'Histoire naturelle de ce Pays. Deuxième Partie (<i>Alcyonium</i> & Porifera). pp 56-63. page(s): 60 [details] additional source Pulitzer-Finali, G.; Pronzato, R. (1976). Report on a Collection of Sponges from the Bay of Naples. II. Keratosa. <em>Pubblicazioni della Stazione zoologica di Napoli.</em> 40(1): 83-104. page(s): 90 [details] Available for editors additional source Pulitzer-Finali, G.; Pronzato, R. (1981 [1980]). The Keratosa in a collection of Mediterranean sponges mainly from the Italian coasts. <em>Annali del Museo civico di storia naturale Giacomo Doria.</em> 83: 127-158. page(s): 137 [details] Available for editors additional source Rützler, K. (1965). Systematik und Ökologie der Poriferen aus Litoral-Schattengebieten der Nordadria. <em>Zeitschrift für Morphologie und Ökologie der Tiere.</em> 55(1): 1-82. page(s): 43-44 [details] Available for editors additional source Sarà, M. (1958). Studio sui Poriferi di una grotta di marea del Golfo di Napoli. <em>Archivo Zoologico Italiano.</em> 43: 203-281, pls I-II. page(s): 273 [details] Available for editors additional source Sarà, M. (1961). La fauna di Poriferi delle grotte delle isole Tremiti. Studio ecologico e sistematico. <em>Archivio zoologico italiano.</em> 46: 1-59,pls I-II. page(s): 55 [details] Available for editors additional source Vacelet, J. (1959). Répartition générale des éponges et systématique des éponges cornées de la région de Marseille et de quelques stations méditerranéennes. <em>Recueil des Travaux de la Station marine d'Endoume.</em> 16 (26): 39-101, pls 1-3. page(s): 76 [details] Available for editors additional source Maldonado, M. (1992). Demosponges of the red coral bottoms from the Alboran Sea. <em>Journal of Natural History.</em> 26: 1131-1161. (look up in IMIS) page(s): 1135 [details] Available for editors additional source Esper, E.J.C. (1794). Die Pflanzenthiere in Abbildungen nach der Natur mit Farben erleuchtet, nebst Beschreibungen. Zweyter Theil. (Raspe: Nürnberg): 1-303. , available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/50841660 page(s): 218-224 [details] additional source Burton, M. (1936). The fishery ground near Alexandria. IX. Sponges. <em>Notes and Memoirs of the Fisheries Research Directorate, Cairo.</em> 17: 1-28. page(s): 24 [details] additional source Rützler, K.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Piantoni, C. (2009). Sponges (Porifera) of the Gulf of Mexico. <i>in</i>: Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. Biodiversity. Texas A & M Press, College Station, Texas. 285–313. note: Misapplication [details] Available for editors additional source Pansini, M. (1987). Report on a collection of Demospongiae from soft bottoms of the Eastern Adriatic Sea. <i>In</i>: Jones WC (ed) European contributions to the taxonomy of sponges. <em>Publications of the Sherkin Island Marine Station.</em> 1, 41-53. page(s): 51 [details] additional source Cruz, T. (2002). Esponjas marinas de Canarias. <em>Consejería de Política Territorial y Medio Ambiente del Gobierno de Canarias.</em> S/C Tenerife. 260 pp. [details] Available for editors additional source Boddaert, P. 1768. Lyst der Plant-Dieren, p. (1-50) + 1-654, pls. 1-14. Van Paddenburg & Van Schoonhoven, Utrecht. page(s): 437 [details] additional source Harmelin, J.-G.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Fichez, R.; Vacelet, J.; Zibrowius, H. (2003). Peuplement de la grotte sous-marine de l'ile de Bagaud (Parc national de Port-Cros, France, Méditerranée). <em>Rapport scientifique du Parc national de Port-Cros.</em> 19: 117-134., available online at https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Nicole_Boury-Esnault/publication/280131013_2003_-_Harmelin_JG_N_Boury-Esnault_R_Fichez_J_Vacelet_H_Zibrowius_Peuplement_de_la_grotte_sous-marine_de_Bagaud_Parc_national_de_Port-Cros_France_Mediterranee_Rapport_scientif page(s): 128 [details] Available for editors additional source Labate, M. (1964). Poriferi di grotta superficiale del litorale adriatico pugliese. <em>Annali del Pontificio Istituto Scienze e Lettere S. Chiara, Napoli.</em> 14, 319-342. page(s): 338 [details] Available for editors additional source Voultsiadou-Koukoura, E.; Koukouras, A. (1993). Contribution to the knowledge of Keratose sponges (Dictyoceratida, Dendroceratida, Verongida: Demospongiae, Porifera) of the Aegean Sea. <em>Mitt. Zool. Mus. Berlin.</em> 69, 57-72. page(s): 58-59 [details] additional source Vacelet, J. (1976). Inventaire des Spongiaires du Parc national de Port-Cros (Var). <em>Travaux scientifiques du Parc national de Port-Cros.</em> 2, 167-186. page(s): 182; note: only 2 small specimens recorded in 1976 [details] Available for editors additional source Kefalas, E.; Castritsi-Catharios, I; Miliou, H. (2003). The impacts of scallop dredging on sponge assemblages in the Gulf of Kalloni (Aegean Sea, northeastern Mediterranean). <em>ICES Journal of Marine Science.</em> 60, 402-10. page(s): 406 [details] Available for editors additional source Topaloğlu, B. (2001). Sponge fauna in the littoral zone of the Marmara Sea. <em>Rapports et Procès Verbaux des Réunions de la Commission Internationale pour l'Exploration de la Mer Méditerranée,.</em> 36, 421. page(s): 421 [details] Available for editors additional source Pansini, M.; Morri, C.; Bianchi, C.N. (2000). The sponge community of a subtidal area with hydrothermal vents: Milos island, Aegean Sea. <em>Estuarine Coastal Shelf Science.</em> 51, 627-635. page(s): 630 [details] Available for editors additional source Corriero, G.; Pansini, M.; Sarà, M. (1984). Sui Poriferi della insenatura della Strea a Porto Cesareo (Lecce). <em>Thalassia Salentina.</em> 14, 1-10. page(s): 8 [details] Available for editors additional source Gerovasileiou, V.; Voultsiadou, E. (2012). Marine Caves of the Mediterranean Sea: A Sponge Biodiversity Reservoir within a Biodiversity Hotspot. <em>PLoS ONE.</em> 7(7): e39873., available online at https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0039873 page(s): Table S1 [details] Available for editors additional source Manconi, R.; Cadeddu, B.; Ledda, F.; Pronzato, R. (2013). An overview of the Mediterranean cave-dwelling horny sponges (Porifera, Demospongiae). <em>ZooKeys.</em> 281: 1-68., available online at https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.281.4171 page(s): 42-43 [details] Available for editors additional source Burton, M. (1934). Notes on some marine Sponges from the Belgian Congo. <em>Revue de Zoologie et de Botanique Africaines.</em> 34 (4), 410-411. note: Misapplication [details] Available for editors additional source Karimi, E.; Ramos, M.; Gonçalves, J.M.S.; Xavier, J.R.; Reis, M.P.; Costa, R. (2017). Comparative Metagenomics Reveals the Distinctive Adaptive Features of the <i>Spongia officinalis</i> Endosymbiotic Consortium. <em>Frontiers in Microbiology.</em> 8 (2499): 1-16., available online at https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02499 page(s): 3 [details] additional source Solórzano, M.R. (1990). Poríferos del litoral gallego: estudio faunístico, distribución e inventario. <em>Phd Thesis Unversidad de Santiago de Compostela.</em> 1036 pp. page(s): 1042-1046; Lám. 137 [details] Available for editors additional source Sitjà, C.; Maldonado, M.; Farias, C.; Rueda, J.L. (2019). Deep-water sponge fauna from the mud volcanoes of the Gulf of Cadiz (North Atlantic, Spain). <em>Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom.</em> 99 (4): 807 - 831., available online at https://doi.org/10.1017/s0025315418000589 page(s): SUP. MAT. appendix 1 [details] Available for editors additional source Díaz, H.; Bevilacqua, M.; Bone, D. (1985). Esponjas en manglares del Parque Nacional Morrocoy. <em>Fondo Editorial Acta Cientifica Venezolanos, Caracas.</em> Pp. 1-62. page(s): 45; note: Misapplication: This is possibly Spongia obliqua. [details] Available for editors additional source Naveiro Millán, A. (2002). Poríferos de la costa da Arrábida (Portugal). Clase Demospongiae. <em>Tesina Unversidad de Santiago de Compostela.</em> 165 pp. page(s): 143-144. Figura 67 [details] Available for editors additional source Vacelet, J. (1991). Statut des éponges commerciales en Méditerranée. pp. 35-42 <i>in</i>: Les espèces marines à protéger en Méditerranée. Boudouresque, C.-F., Avon, M., & Graves, V. (eds) Gis Posidonie publication, France. page(s): 35 [details] Available for editors status source Bowerbank, J.S. (1862). On the Anatomy and Physiology of the Spongiadae. Part III On the Generic Characters, the Specific Characters, and on the Method of Examination. <em>Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society.</em> 152(2): 1087-1135, pls LXXII-LXXIV. page(s): 1119 [details] toxicology source Perez, T.; Wafo, E.; Fourt, M.; Vacelet, J. (2003). Marine Sponges as Biomonitor of Polychlorobiphenyl Contamination: Concentration and Fate of 24 Congeners. <em>Environmental Science & Technology.</em> 37(10): 2152-2158., available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/es026234v [details] Available for editors toxicology source Perez, T.; Longet, D.; Schembri, T.; Rebouillon, P.; Vacelet, J. (2005). Effects of 12 years' operation of a sewage treatment plant on trace metal occurrence within a Mediterranean commercial sponge (<i>Spongia officinalis</i>, Demospongiae). <em>Marine Pollution Bulletin.</em> 50(3): 301-309., available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.11.001 [details] Available for editors biology source Vacelet, J.; Vacelet, E.; Gaino, E.; Gallissian, M.-F. (1994). Bacterial attack of spongin skeleton during the 1986-1990 Mediterranean sponge disease. <i>in</i>: Sponges in Time and Space, van Soest, van Kempen & Braekman (eds) Balkema. Rotterdam. pp 355-362. page(s): 358-359 [details] Available for editors  Present Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate Inaccurate  Introduced: alien Introduced: alien  Containing type locality Containing type locality
From editor or global species database
Biology 1986-1990 Mediterranean sponge disease: Bacterial attack of spongin fibers [details]
To Barcode of Life (6 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (166 publications) To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL) To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Spongia officinalis) To GenBank (18029 nucleotides; 12 proteins) To PESI To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Porifera Collection (1 record) To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Porifera Collection (2 records) To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Porifera Collection (3 records) To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Porifera Collection (4 records) To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Porifera Collection (9 records) To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Porifera Collection (Holotype USNM 23200) To Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History (YPM IZ 008561.PR) To ITIS |