WRiMS taxon details
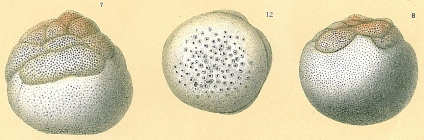
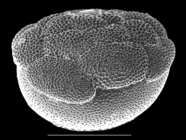
Cymbaloporetta plana (Cushman, 1924)
595519 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:595519)
accepted
Species
marine, brackish, fresh, terrestrial
recent only
(of ) Cushman, J. A. (1924). Samoan foraminifera. <em>Publications of the Carnegie Institution of Washington, Department of Marine Biology.</em> 21(342): 1-75. [details] Available for editors 
Hayward, B.W.; Le Coze, F.; Vachard, D.; Gross, O. (2024). World Foraminifera Database. Cymbaloporetta plana (Cushman, 1924). Accessed through: Costello, M. J.; Ahyong, S.; Bieler, R.; Boudouresque, C.; Desiderato, A.; Downey, R.; Galil, B. S.; Gollasch, S.; Hutchings, P.; Kamburska, L.; Katsanevakis, S.; Kupriyanova, E.; Lejeusne, C.; Ma, K. C. K.; Marchini, A.; Occhipinti, A.; Pagad, S.; Panov, V. E.; Poore, G. C. B.; Rewicz, T.; Robinson, T. B.; Rius, M.; Sobczyk, R.; Stern, N.; Turon, X.; Valls Domedel, G.; Verleye, T.; Vieira, L. M.; Willan, R. C.; Yeo Chong Jinn, D.; Zhan, A. (2024) World Register of Introduced Marine Species (WRiMS) at: https://www.marinespecies.org/introduced/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=595519 on 2025-04-03
Costello, M. J.; Ahyong, S.; Bieler, R.; Boudouresque, C.; Desiderato, A.; Downey, R.; Galil, B. S.; Gollasch, S.; Hutchings, P.; Kamburska, L.; Katsanevakis, S.; Kupriyanova, E.; Lejeusne, C.; Ma, K. C. K.; Marchini, A.; Occhipinti, A.; Pagad, S.; Pino, L.; Poore, G. C. B.; Rewicz, T.; Rius, M.; Robinson, T. B.; Sobczyk, R.; Stępień, A.; Turon, X.; Valls Domedel, G.; Verleye, T.; Vieira, L. M.; Willan, R. C.; Zhan, A. (2025). World Register of Introduced Marine Species (WRiMS). Cymbaloporetta plana (Cushman, 1924). Accessed at: https://marinespecies.org/introduced%20/aphia.php/api-docs/docs/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=595519 on 2025-04-03
Date
action
by
original description
(of ) Cushman, J. A. (1924). Samoan foraminifera. <em>Publications of the Carnegie Institution of Washington, Department of Marine Biology.</em> 21(342): 1-75. [details] Available for editors 
context source (Introduced species) Katsanevakis, S.; Bogucarskis, K.; Gatto, F.; Vandekerkhove, J.; Deriu, I.; Cardoso A.S. (2012). Building the European Alien Species Information Network (EASIN): a novel approach for the exploration of distributed alien species data. <em>BioInvasions Records.</em> 1: 235-245., available online at http://easin.jrc.ec.europa.eu [details] Available for editors
context source (HKRMS) Yim, W. W.-S.; He, X.-X. (1988). Holocene foraminifera in Hong Kong and their palaeoenvironmental significance. <em>In: The palaeoenvironment of east asia from the mid-tertiary, Proceedings of the Second International Conference on the Paleoenvironment of East Asia, Vol. II: Oceanography, Palaeozoology and Palaeoanthropology (eds. Whyte, P. Aigner, J.S., Jablonski, N.G., Taylor, G., Walker, D., Pinxian, W. & So, C.-L.), Centre of Asian Studies, University of Hong Kong.</em> 787-809. [details] Available for editors
additional source Zenetos, A., S. Gofas, M. Verlaque, M. Cinar, J. Garcia Raso, C. Bianchi, C. Morri, E. Azzurro, M. Bilecenoglu, C. Froglia, I. Siokou, D. Violanti, A. Sfriso, G. San Martin, A. Giangrande, T. Katagan, E. Ballesteros, A. Ramos-Espla, F. Mastrototaro, O. Ocana, A. Zingone, M,. Gambi & N. Streftaris. (2010). Alien species in the Mediterranean Sea by 2010. A contribution to the application of European Union's Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). Part I. Spatial distribution. <em>Mediterranean Marine Science.</em> 11(2): 381-493., available online at https://doi.org/10.12681/mms.87 [details]
additional source Zenetos, A., E. Meric, M. Verlaque, P. Galli, C.F. Boudouresque, A. Giangrande, M. Cinar & M. Bilecenoglu. (2008). Additions to the annotated list of marine alien biota in the Mediterranean with special emphasis on Foraminifera and Parasites. <em>Mediterranean Marine Science.</em> 9(1): 119-165., available online at https://doi.org/10.12681/mms.146 [details] Available for editors
context source (Introduced species) Katsanevakis, S.; Bogucarskis, K.; Gatto, F.; Vandekerkhove, J.; Deriu, I.; Cardoso A.S. (2012). Building the European Alien Species Information Network (EASIN): a novel approach for the exploration of distributed alien species data. <em>BioInvasions Records.</em> 1: 235-245., available online at http://easin.jrc.ec.europa.eu [details] Available for editors
context source (HKRMS) Yim, W. W.-S.; He, X.-X. (1988). Holocene foraminifera in Hong Kong and their palaeoenvironmental significance. <em>In: The palaeoenvironment of east asia from the mid-tertiary, Proceedings of the Second International Conference on the Paleoenvironment of East Asia, Vol. II: Oceanography, Palaeozoology and Palaeoanthropology (eds. Whyte, P. Aigner, J.S., Jablonski, N.G., Taylor, G., Walker, D., Pinxian, W. & So, C.-L.), Centre of Asian Studies, University of Hong Kong.</em> 787-809. [details] Available for editors
additional source Zenetos, A., S. Gofas, M. Verlaque, M. Cinar, J. Garcia Raso, C. Bianchi, C. Morri, E. Azzurro, M. Bilecenoglu, C. Froglia, I. Siokou, D. Violanti, A. Sfriso, G. San Martin, A. Giangrande, T. Katagan, E. Ballesteros, A. Ramos-Espla, F. Mastrototaro, O. Ocana, A. Zingone, M,. Gambi & N. Streftaris. (2010). Alien species in the Mediterranean Sea by 2010. A contribution to the application of European Union's Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). Part I. Spatial distribution. <em>Mediterranean Marine Science.</em> 11(2): 381-493., available online at https://doi.org/10.12681/mms.87 [details]
additional source Zenetos, A., E. Meric, M. Verlaque, P. Galli, C.F. Boudouresque, A. Giangrande, M. Cinar & M. Bilecenoglu. (2008). Additions to the annotated list of marine alien biota in the Mediterranean with special emphasis on Foraminifera and Parasites. <em>Mediterranean Marine Science.</em> 9(1): 119-165., available online at https://doi.org/10.12681/mms.146 [details] Available for editors
 Present
Present  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
From regional or thematic species database
Introduced species abundance in Greek part of the Aegean Sea (Marine Region) : Rare [details]Introduced species impact in Greek part of the Aegean Sea (Marine Region) : Other impact - undefined or uncertain [details]
Introduced species remark In Greek part of the Aegean Sea (Marine Region) : The species is present in the Adriatic and Tyrrhenian Seas and the coasts of Turkey (see Koukousioura et al. 2010).The study conducted by Koukousioura et al. 2010 are the first reports of the species in Greek waters. [details]
Introduced species vector dispersal in Italian part of the Tyrrhenian Sea (Marine Region) : Shipping [details]
Introduced species vector dispersal in Greek part of the Aegean Sea (Marine Region) : Ships: accidental with ballast water, sea water systems, live wells or other deck basins
Could have entered via Gibraltar from the Atlantic Ocean populations or via the Suez Canal [details]