| About | | Search taxa | | Taxon tree | | Search literature | | Checklist | | Stats | | Log in |
WoRMS taxon detailsGambierdiscus toxicus R.Adachi & Y.Fukuyo, 1979
233382 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:233382)
accepted
Species
marine,
Adachi R. & Fukuyo Y. 1979. The thecal structure of a marine toxic dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus gen. et sp. nov. collected in a ciguatera endemic area. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 45: 67-71., available online at https://doi.org/10.2331/suisan.45.67 [details]
Type locality contained in Ile Mangareva
type locality contained in Ile Mangareva [details]
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:44999
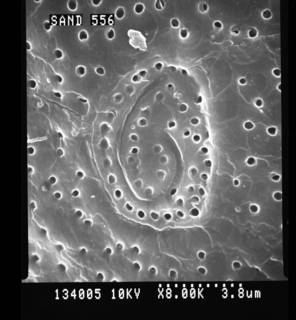
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:44999 [details] Description Lens-shaped, anterio-posteriorly compressed. Thecal surface covered with evenly distributed fine pores. Apical pore plate...
Description Lens-shaped, anterio-posteriorly compressed. Thecal surface covered with evenly distributed fine pores. Apical pore plate oval containing fish-hook shaped pore. 2’ largest apical plate, precingular 1’ smallest. 1p plate broad, hatchet-shaped. [details]
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway (taxonomic information republished from AlgaeBase with permission of M.D. Guiry). Gambierdiscus toxicus R.Adachi & Y.Fukuyo, 1979. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=233382 on 2025-05-03
Date action by 2006-07-27 06:59:07Z created Camba Reu, Cibran 2015-06-26 12:00:51Z changed db_admin Copyright notice: the information originating from AlgaeBase may not be downloaded or replicated by any means, without the written permission of the copyright owner (generally AlgaeBase). Fair usage of data in scientific publications is permitted. Nomenclatureoriginal description
Adachi R. & Fukuyo Y. 1979. The thecal structure of a marine toxic dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus gen. et sp. nov. collected in a ciguatera endemic area. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 45: 67-71., available online at https://doi.org/10.2331/suisan.45.67 [details] basis of record Gómez, F. (2005). A list of free-living dinoflagellate species in the world's oceans. <em>Acta Bot. Croat.</em> 64(1): 129-212. [details] Ecologyecology source
Leles, S. G.; Mitra, A.; Flynn, K. J.; Tillmann, U.; Stoecker, D.; Jeong, H. J.; Burkholder, J.; Hansen, P. J.; Caron, D. A.; Glibert, P. M.; Hallegraeff, G.; Raven, J. A.; Sanders, R. W.; Zubkov, M. (2019). Sampling bias misrepresents the biogeographical significance of constitutive mixotrophs across global oceans. <em>Global Ecology and Biogeography.</em> 28(4): 418-428., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12853 [details] Available for editors ecology source Mitra, A.; Caron, D. A.; Faure, E.; Flynn, K. J.; Leles, S. G.; Hansen, P. J.; McManus, G. B.; Not, F.; Do Rosario Gomes, H.; Santoferrara, L. F.; Stoecker, D. K.; Tillmann, U. (2023). The Mixoplankton Database (MDB): Diversity of photo‐phago‐trophic plankton in form, function, and distribution across the global ocean. <em>Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology.</em> 70(4)., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12972 [details] ecology source Faust, M.A. (1998). Mixotrophy in tropical benthic dinoflagellates. In: Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernandez, L., Wyatt, T. (Eds.), Harmful Algae. Proceedings of the VIII International Conference on Harmful Algae, Vigo, Spain, 1997, Xunta de Galicia and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO, Paris, France, pp. 390–393. [details] Otheradditional source
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. <em>World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway.</em> searched on YYYY-MM-DD., available online at http://www.algaebase.org [details]
additional source Tomas, C.R. (Ed.). (1997). Identifying marine phytoplankton. Academic Press: San Diego, CA [etc.] (USA). ISBN 0-12-693018-X. XV, 858 pp., available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/book/9780126930184 [details] additional source Murata M., Legrand A.M., Ishibashi Y., Fukui M. & Yasumoto T. 1990. Structures and configurations of ciguatoxin from the moray eel <i>Gymnothorax javanicus</i> and its likely precursor from the dinoflagellate <i>Gambierdiscus toxicus</i>. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 112: 4380-4386. [details] additional source Satake M., Murata M. & Yasumoto T. 1993. The structure of CTX3C, a ciguatoxin congener isolated from cultured <i>Gambierdiscus toxicus</i>. Tetrahedron Lett. 34: 1975-1978. [details] additional source Yasumoto T. & Satake M. 1996. Chemistry, etiology and determination methods of ciguatera toxins. J. Toxicol. 15: 91-107. [details] additional source Steidinger, K. A., M. A. Faust, and D. U. Hernández-Becerril. 2009. Dinoflagellates (Dinoflagellata) of the Gulf of Mexico, Pp. 131–154 in Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. Biodiversity. Texas A&M Press, College [details] additional source Litaker, R.W., Vandersea, M.W., Faust, M.A., Kibler, S.R., Chinain, M., Holmes, M.J., Holland, W.C. & Tester, P.A. 2009. Taxonomy of <i>Gambierdiscus</i> including four new species, <i>Gambierdiscus caribaeus</i>, <i>Gambierdiscus carolianus</i>, <i>Gambierdiscus carpenteri</i> and <i>Gambierdiscus ruetzleri</i> (Gonyaulacales, Dinophyceae). Phycologia, 48: 344-90 [details] Available for editors additional source Lewis R.J. 2001. The changing face of ciguatera. Toxicon 39: 97-106., available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/s0041-0101(00)00161-6 [details] additional source Moestrup, Ø., Akselman, R., Cronberg, G., Elbraechter, M., Fraga, S., Halim, Y., Hansen, G., Hoppenrath, M., Larsen, J., Lundholm, N., Nguyen, L. N., Zingone, A. (Eds) (2009 onwards). IOC-UNESCO Taxonomic Reference List of Harmful Micro Algae., available online at http://www.marinespecies.org/HAB [details] additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors additional source Chang, F.H.; Charleston, W.A.G.; McKenna, P.B.; Clowes, C.D.; Wilson, G.J.; Broady, P.A. (2012). Phylum Myzozoa: dinoflagellates, perkinsids, ellobiopsids, sporozoans, in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2012). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 3. Kingdoms Bacteria, Protozoa, Chromista, Plantae, Fungi. pp. 175-216. [details]  Present Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate Inaccurate  Introduced: alien Introduced: alien  Containing type locality Containing type locality
From editor or global species database
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:44999 [details]From regional or thematic species database
Description Lens-shaped, anterio-posteriorly compressed. Thecal surface covered with evenly distributed fine pores. Apical pore plate oval containing fish-hook shaped pore. 2’ largest apical plate, precingular 1’ smallest. 1p plate broad, hatchet-shaped. [details] Harmful effect The taxonomy of the genus Gambierdiscus has undergone drastic changes and many reports of toxicity using the name Gambierdiscus toxicus have been shown to refer to other species. G. toxicus is, however, toxic, material with significant maitotoxicity as assessed by mouse bioassay has been found in Tahiti Lagoon (Kohli et al. 2015). Toxic material therefore probably also occurs elsewhere. [details] |