WoRMS taxon details
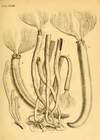
Sabella spallanzanii (Gmelin, 1791)
130969 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:130969)
accepted
Species
Amphitrite ventilabrum Gmelin, 1791 in Linnaeus · unaccepted (subjective synonym)
Amphitrite ventilabrum [sensu Lamarck, 1818] · unaccepted (unstated, but evidently a usage...)
unstated, but evidently a usage of Gmelin's 1791 name
Corallina Tubularia-Melitensis Ellis, 1755 · unaccepted (subjective synonym)
Nereis lutraria Pallas, 1766 · unaccepted (subjective synonym)
Sabella gracillima Kinberg, 1866 · unaccepted (subjective synonym)
Sabella penicillum [auct. misspelling] · unaccepted (lapsus for penicillus)
Sabella penicillus (Linnaeus, 1758) · unaccepted (superseded recombination of...)
superseded recombination of subjective synonym
Sabella unispira Cuvier, 1816 · unaccepted (subjective synonym)
Sabella ventilabrum (Gmelin in Linnaeus, 1791) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym (superseded subsequent combination...)
superseded subsequent combination of subjective synonym
Sabella viridis Milne Edwards in Quatrefages, 1866 · unaccepted (subjective synonym)
Serpula penicillus Linnaeus, 1758 · unaccepted (subjective synonym)
Spirographis elegans Quatrefages, 1866 · unaccepted (subjective synonym)
Spirographis gracilis Hansen, 1882 · unaccepted (subjective synonym)
Spirographis imperialis Hansen, 1882 · unaccepted (subjective synonym)
Spirographis longispira Quatrefages, 1866 · unaccepted (subjective synonym)
Spirographis spallanzanii (Gmelin, 1791) · unaccepted (genus is a subjective synonym of...)
genus is a subjective synonym of Sabella
Tubularia spallanzanii Gmelin, 1791 · unaccepted (basionym)
marine, brackish, fresh, terrestrial
recent only
(of Tubularia spallanzanii Gmelin, 1791) Gmelin, J. F. (1791). Caroli a Linné Systema Naturae, ed. 13. Tome 1(6). Vermes. G. E. Beer, Lipsiae [Leipzig]. pp. 3021-3910. , available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/83098#5
page(s): 3834 [details]
page(s): 3834 [details]
Type locality contained in Mediterranean Sea
type locality contained in Mediterranean Sea [from synonym] [view taxon] [details]
Distribution Knight-Jones & Perkins (1998) placed Sabella gracillima Kinberg, 1867 from Rio de Janeiro, and four names in Spirographis...
Distribution Knight-Jones & Perkins (1998) placed Sabella gracillima Kinberg, 1867 from Rio de Janeiro, and four names in Spirographis erected by Hansen, one from Rio, and a further species, Spirographis braziliensis Treadwell, 1932, all as synonyms of Sabella spallanzanii. It is not clear if they examined the types. So, apparently Sabella spallanzanii did occur around Rio de Janeiro in the mid 19th C. There are no modern reports, which seems unusual with such a conspicuous worm unless the population has died out. [details]
Read, G.; Fauchald, K. (Ed.) (2026). World Polychaeta Database. Sabella spallanzanii (Gmelin, 1791). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=130969 on 2026-01-16
Date
action
by
![]() The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 License
The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 License
Nomenclature
original description
(of Amphitrite ventilabrum Gmelin, 1791 in Linnaeus) Linnaeus, C. (1788). Systema Naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus differentiis, synonymis, locis. [The system of nature through the three kingdoms of nature, according to classes, orders, genera, species, with characteristic differences, synonyms, and places.]. <em>Editio decima tertia, aucta reformata. Cura J.F. Gmelin. G.E. Beer, Lipsiae.</em> 1(5-6):2225-3909., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/2896589
note: Knight-Jones uses 1791 for the part 6 volume [details]
original description (of Nereis lutraria Pallas, 1766) Pallas, P.S. (1766) Miscellanea zoologica. Quibus novae imprimis atque obscurae animalium species describuntur et observationibus iconibusque illustrantur. Petrum van Cleef. Hagí Comitum., xii + 224 pp.;14 pls., available online at https://archive.org/details/pspallasmedicina00pall [details]
original description (of Sabella gracillima Kinberg, 1866) Kinberg, J.G.H. (1866 [or 1867]). Annulata nova. [Continuatio.]. <em>Öfversigt af Königlich Vetenskapsakademiens förhandlingar, Stockholm.</em> 23(9): 337-357., available online at http://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/32287795
page(s): 353 [details]
original description (of Sabella unispira Cuvier, 1816) Cuvier, G. (1816). Le Règne Animal distribué d'après son organisation, pour servir de base à l'histoire naturelle des animaux et d'introduction à l'anatomie comparée. Tome II, contenant les reptiles, les poissons, les mollusques et les annélides. Deterville, Paris, pp. i-xviii, 1-532 [pls. 9-10 contained in volume 4]. , available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/1848835
page(s): 519; note: new name for Spirographis spallanzanii (Gmelin, 1791) sensu Viviani, 1805 [details]
original description (of Spirographis elegans Quatrefages, 1866) Quatrefages, A. de. (1866 (1865)). Histoire naturelle des Annelés marins et d'eau douce. Annélides et Géphyriens. <em>Librarie Encyclopédique de Roret. Paris.</em> <b>Volume 1.</b> 1-588., available online at http://books.google.com/books?id=FV9IAAAAYAAJ [details]
original description (of Spirographis gracilis Hansen, 1882) Hansen, A. (1882). Recherches sur les annélides recueillies par M. le professeur Édouard van Benedon pendant son voyage au Brésil et à la Plata. <em>Mémoires Couronnes et Mémoires des Savants Etrangers publiés par L'Académie Royale des Sciences, des Lettres et des Beaux-Arts de Belgique.</em> 44(3): 1-29., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/5943290
page(s): 21, plate VII figs. 6-8 [details]
original description (of Spirographis imperialis Hansen, 1882) Hansen, A. (1882). Recherches sur les annélides recueillies par M. le professeur Édouard van Benedon pendant son voyage au Brésil et à la Plata. <em>Mémoires Couronnes et Mémoires des Savants Etrangers publiés par L'Académie Royale des Sciences, des Lettres et des Beaux-Arts de Belgique.</em> 44(3): 1-29., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/5943290
page(s): 21-22, plate VII figs. 9-12 [details]
original description (of Spirographis longispira Quatrefages, 1866) Quatrefages, A. de. (1866 (1865)). Histoire naturelle des Annelés marins et d'eau douce. Annélides et Géphyriens. <em>Librarie Encyclopédique de Roret. Paris.</em> <b>Volume 1.</b> 1-588., available online at http://books.google.com/books?id=FV9IAAAAYAAJ [details]
original description (of Sabella viridis Milne Edwards in Quatrefages, 1866) McIntosh, W. C. (1874). On the invertebrate marine fauna and fishes of St. Andrews [part of several parts, 2nd part of Class Annelida. Includes all of Polychaeta. <em>Annals and Magazine of Natural History.</em> 14: 192-207 (4th series) issue 80 part 28., available online at http://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/19210023 [details]
original description (of Sabella viridis Milne Edwards in Quatrefages, 1866) Quatrefages, A. de. (1866 (1865)). Histoire naturelle des Annelés marins et d'eau douce. Annélides et Géphyriens. <em>Librarie Encyclopédique de Roret. Paris.</em> <b>Volume 1.</b> 1-588., available online at http://books.google.com/books?id=FV9IAAAAYAAJ [details]
original description (of Serpula penicillus Linnaeus, 1758) Linnaeus, C. (1758). Systema Naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. [The system of nature through the three kingdoms of nature, according to classes, orders, genera, species, with characters, differences, synonyms, places.]. <em>Impensis Direct. Laurentii Salvii. Holmiae [Stockholm].</em> 1(10) [iii], 824 p., available online at https://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/726886
page(s): 788 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
original description (of Corallina Tubularia-Melitensis Ellis, 1755) Ellis, J., 1755. An essay towards a natural history of the corallines, and other marine productions of the like kind, commonly found on the coasts of Great Britain and Ireland., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/10676206
page(s): 92 [details]
original description (of Tubularia spallanzanii Gmelin, 1791) Gmelin, J. F. (1791). Caroli a Linné Systema Naturae, ed. 13. Tome 1(6). Vermes. G. E. Beer, Lipsiae [Leipzig]. pp. 3021-3910. , available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/83098#5
page(s): 3834 [details]
note: Knight-Jones uses 1791 for the part 6 volume [details]
original description (of Nereis lutraria Pallas, 1766) Pallas, P.S. (1766) Miscellanea zoologica. Quibus novae imprimis atque obscurae animalium species describuntur et observationibus iconibusque illustrantur. Petrum van Cleef. Hagí Comitum., xii + 224 pp.;14 pls., available online at https://archive.org/details/pspallasmedicina00pall [details]
original description (of Sabella gracillima Kinberg, 1866) Kinberg, J.G.H. (1866 [or 1867]). Annulata nova. [Continuatio.]. <em>Öfversigt af Königlich Vetenskapsakademiens förhandlingar, Stockholm.</em> 23(9): 337-357., available online at http://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/32287795
page(s): 353 [details]
original description (of Sabella unispira Cuvier, 1816) Cuvier, G. (1816). Le Règne Animal distribué d'après son organisation, pour servir de base à l'histoire naturelle des animaux et d'introduction à l'anatomie comparée. Tome II, contenant les reptiles, les poissons, les mollusques et les annélides. Deterville, Paris, pp. i-xviii, 1-532 [pls. 9-10 contained in volume 4]. , available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/1848835
page(s): 519; note: new name for Spirographis spallanzanii (Gmelin, 1791) sensu Viviani, 1805 [details]
original description (of Spirographis elegans Quatrefages, 1866) Quatrefages, A. de. (1866 (1865)). Histoire naturelle des Annelés marins et d'eau douce. Annélides et Géphyriens. <em>Librarie Encyclopédique de Roret. Paris.</em> <b>Volume 1.</b> 1-588., available online at http://books.google.com/books?id=FV9IAAAAYAAJ [details]
original description (of Spirographis gracilis Hansen, 1882) Hansen, A. (1882). Recherches sur les annélides recueillies par M. le professeur Édouard van Benedon pendant son voyage au Brésil et à la Plata. <em>Mémoires Couronnes et Mémoires des Savants Etrangers publiés par L'Académie Royale des Sciences, des Lettres et des Beaux-Arts de Belgique.</em> 44(3): 1-29., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/5943290
page(s): 21, plate VII figs. 6-8 [details]
original description (of Spirographis imperialis Hansen, 1882) Hansen, A. (1882). Recherches sur les annélides recueillies par M. le professeur Édouard van Benedon pendant son voyage au Brésil et à la Plata. <em>Mémoires Couronnes et Mémoires des Savants Etrangers publiés par L'Académie Royale des Sciences, des Lettres et des Beaux-Arts de Belgique.</em> 44(3): 1-29., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/5943290
page(s): 21-22, plate VII figs. 9-12 [details]
original description (of Spirographis longispira Quatrefages, 1866) Quatrefages, A. de. (1866 (1865)). Histoire naturelle des Annelés marins et d'eau douce. Annélides et Géphyriens. <em>Librarie Encyclopédique de Roret. Paris.</em> <b>Volume 1.</b> 1-588., available online at http://books.google.com/books?id=FV9IAAAAYAAJ [details]
original description (of Sabella viridis Milne Edwards in Quatrefages, 1866) McIntosh, W. C. (1874). On the invertebrate marine fauna and fishes of St. Andrews [part of several parts, 2nd part of Class Annelida. Includes all of Polychaeta. <em>Annals and Magazine of Natural History.</em> 14: 192-207 (4th series) issue 80 part 28., available online at http://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/19210023 [details]
original description (of Sabella viridis Milne Edwards in Quatrefages, 1866) Quatrefages, A. de. (1866 (1865)). Histoire naturelle des Annelés marins et d'eau douce. Annélides et Géphyriens. <em>Librarie Encyclopédique de Roret. Paris.</em> <b>Volume 1.</b> 1-588., available online at http://books.google.com/books?id=FV9IAAAAYAAJ [details]
original description (of Serpula penicillus Linnaeus, 1758) Linnaeus, C. (1758). Systema Naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. [The system of nature through the three kingdoms of nature, according to classes, orders, genera, species, with characters, differences, synonyms, places.]. <em>Impensis Direct. Laurentii Salvii. Holmiae [Stockholm].</em> 1(10) [iii], 824 p., available online at https://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/726886
page(s): 788 [details] Available for editors
original description (of Corallina Tubularia-Melitensis Ellis, 1755) Ellis, J., 1755. An essay towards a natural history of the corallines, and other marine productions of the like kind, commonly found on the coasts of Great Britain and Ireland., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/10676206
page(s): 92 [details]
original description (of Tubularia spallanzanii Gmelin, 1791) Gmelin, J. F. (1791). Caroli a Linné Systema Naturae, ed. 13. Tome 1(6). Vermes. G. E. Beer, Lipsiae [Leipzig]. pp. 3021-3910. , available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/83098#5
page(s): 3834 [details]
Taxonomy
redescription
Knight-Jones, Phyllis; Perkins, Thomas H. (1998). A revision of Sabella, Bispira and Stylomma (Polychaeta: Sabellidae). <em>Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, London.</em> 123: 385-467., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.1998.tb01370.x
note: includes analysis of the status of competing names [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
note: includes analysis of the status of competing names [details] Available for editors
Ecology
ecology source
Read, G. B.; Inglis, G.; Stratford, P.; Ahyong, S. T. (2011). Arrival of the alien fanworm Sabella spallanzanii (Gmelin, 1791) (Polychaeta: Sabellidae) in two New Zealand harbours. <em>Aquatic Invasions.</em> 6(3): 273-279., available online at http://www.aquaticinvasions.net/2011/AI_2011_6_3_Read_etal.pdf [details] 
Other
additional source
Biosis; Index To Organism Names, available online at http://www.biosis.org.uk/ion/results.asp [details]
additional source Bellan, G. (2001). Polychaeta, <i>in</i>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. <em>Collection Patrimoines Naturels.</em> 50: 214-231. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Fattorini, Daniele and Regoli, Francesco 2006. Arsenic speciation in tissues of the Mediterranean Polychaete Sabella spallanzanii. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 23(8):1881-1887 [details]
additional source Wilson, R.S.; Hutchings, P.A. and Glasby, C.J. (eds) 2003. List of Polychaete species introduced to Australia. Polychaetes: An Interactive Identification Guide. CSIRO Publishing, Melbourne [details]
additional source Brine, O.; Hunt, L.; Costello, M. J. (2013). Marine biofouling on recreational boats on swing moorings and berths. <em>Management of Biological Invasions.</em> 4(4): 327-341., available online at https://doi.org/10.3391/mbi.2013.4.4.07 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Bellan, G. (2001). Polychaeta, <i>in</i>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. <em>Collection Patrimoines Naturels.</em> 50: 214-231. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Fattorini, Daniele and Regoli, Francesco 2006. Arsenic speciation in tissues of the Mediterranean Polychaete Sabella spallanzanii. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 23(8):1881-1887 [details]
additional source Wilson, R.S.; Hutchings, P.A. and Glasby, C.J. (eds) 2003. List of Polychaete species introduced to Australia. Polychaetes: An Interactive Identification Guide. CSIRO Publishing, Melbourne [details]
additional source Brine, O.; Hunt, L.; Costello, M. J. (2013). Marine biofouling on recreational boats on swing moorings and berths. <em>Management of Biological Invasions.</em> 4(4): 327-341., available online at https://doi.org/10.3391/mbi.2013.4.4.07 [details] Available for editors
 Present
Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio
Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
From editor or global species database
Diagnosis The original description as Tubularia spallanzanii Gmelin 1791 is as follows: "Cirris quinis plumosis utrinque pectinatis, tubulo cylindrico corneo inferne incurvo [= Five feathery circles combed on each side, with a horny cylindrical tube incurved below.]. Müller's 1776 brief diagnosis of Tubularia penicillus is closely similar to this later diagnosis for Serpula penicillus in Gmelin. [details]Distribution Knight-Jones & Perkins (1998) placed Sabella gracillima Kinberg, 1867 from Rio de Janeiro, and four names in Spirographis erected by Hansen, one from Rio, and a further species, Spirographis braziliensis Treadwell, 1932, all as synonyms of Sabella spallanzanii. It is not clear if they examined the types. So, apparently Sabella spallanzanii did occur around Rio de Janeiro in the mid 19th C. There are no modern reports, which seems unusual with such a conspicuous worm unless the population has died out. [details]
Synonymy It is obvious strict priority is not being observed here. Synonymies of "spallanzanii" usages are very complex and resolving them in WoRMS is not yet complete. Please see Knight-Jones and Perkins (1998) for full background. Those authors designated a single neotype for the four names Tubularia spallanzanii Gmelin, Serpula penicillus Linnaeus, Teredo melitensis Bergius, and Amphitrite ventilabrum Gmelin, the last three of which they placed junior to Tubularia spallanzanii [now Sabella spallanzanii] to stabilise the well-known name. An application to ICZN to confirm this was proposed, but did not occur. They intended to "to ask the International Commission of Zoological Nomenclature to use its plenary powers to stabilize the current specific name of the well-known species Sabella spallanzanii by suppressing Serpula penicillus, Teredo melitensis Bergius, and Amphitrite ventilabrum Gmelin, its early synonyms". Strictly Sabella penicillus should remain the valid name. If 'penicillus', as Latin diminutive for painter's brush, is treated as a noun in apposition, its suffix is not changed. [details]
Type designation Neotype, designated Knight-Jones & Perkins (1998), Natural History Museum London, NHM 1929.12.23.1, collected Malta, exact location unknown, by B. Grey [details]
From regional or thematic species database
Introduced species impact in Australian part of the Bass Strait (Marine Region) : Other impact - undefined or uncertain [details]Introduced species management in Australian part of the Bass Strait (Marine Region) : yes [details]
Introduced species management New Zealand part of the South Pacific Ocean (Marine Region) Specimens of S. spallanzanii were collected
from within the Auckland region and exposed to salinity treatments for up to 1440 min (24 h) and mortality rates were compared using LT50 i.e. number of minutes taken for 50% of worms to die. Specimens subjected to hypo-saline conditions resulted in an LT50 of 31.0 min compared to 132.0 min for hyper-saline conditions. Accordingly, hypo-saline dips have potential as an environmentally safe and cost-effective management method for maintenance of recreational vessels and other marine structures (e.g. aquaculture gear and shellfish stocks) that are heavily fouled with S. spallanzanii. [details]
Introduced species management in New Zealand part of the South Pacific Ocean (Marine Region) : yes [details]
Introduced species vector dispersal in Australian part of the Bass Strait (Marine Region) : Ships: accidental as attached or free-living fouling organisms [details]
Introduced species vector dispersal in Australia (Nation) : Ships: accidental with ballast water, sea water systems, live wells or other deck basins [details]
| Language | Name | |
|---|---|---|
| Catalan | palmeretaespirògraf | [details] |
| English | Mediterranean fanwormfeather-duster wormfeather duster wormfanwormEuropean fan worm | [details] |
| French | spirographe | [details] |
| German | SchraubensabelleSchrauben SabelleGroßer Fächerwurm | [details] |
| Italian | spirografoombrella di mare | [details] |
| Spanish | plumero de mar | [details] |
To Barcode of Life (70 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (1 publication) (from synonym Sabella gracillima Kinberg, 1866)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (4 publications) (from synonym Spirographis longispira Quatrefages, 1866)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (50 publications) (from synonym Spirographis spallanzanii (Gmelin, 1791))
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (7 publications)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (93 publications) (from synonym Sabella penicillus (Linnaeus, 1758))
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Sabella spallanzanii)
To GenBank (91 nucleotides; 128 proteins) (from synonym Sabella penicillus (Linnaeus, 1758))
To GenBank (91 nucleotides; 128 proteins)
To Global Invasive Species Database (GISD)
To Information system on Aquatic Non-Indigenous and Cryptogenic Species (AquaNIS)
To PESI
To PESI (from synonym Sabella penicillus (Linnaeus, 1758))
To PESI (from synonym Spirographis spallanzanii (Gmelin, 1791))
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Annelida Collection (1 record) (from synonym Sabella penicillus (Linnaeus, 1758))
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Annelida Collection (8 records)
To ITIS
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (1 publication) (from synonym Sabella gracillima Kinberg, 1866)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (4 publications) (from synonym Spirographis longispira Quatrefages, 1866)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (50 publications) (from synonym Spirographis spallanzanii (Gmelin, 1791))
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (7 publications)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (93 publications) (from synonym Sabella penicillus (Linnaeus, 1758))
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Sabella spallanzanii)
To GenBank (91 nucleotides; 128 proteins) (from synonym Sabella penicillus (Linnaeus, 1758))
To GenBank (91 nucleotides; 128 proteins)
To Global Invasive Species Database (GISD)
To Information system on Aquatic Non-Indigenous and Cryptogenic Species (AquaNIS)
To PESI
To PESI (from synonym Sabella penicillus (Linnaeus, 1758))
To PESI (from synonym Spirographis spallanzanii (Gmelin, 1791))
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Annelida Collection (1 record) (from synonym Sabella penicillus (Linnaeus, 1758))
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Annelida Collection (8 records)
To ITIS