| Intro | | Search taxa | | Browse taxa | | Distributions | | Terminology | | References | | Statistics | | Online sources | | Tutorial | | Log in |
WoRMS taxon detailsPyrodinium bahamense var. compressum (Böhm) Steidinger, Tester & F.J.R.Taylor, 1980
233399 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:233399)
accepted
Variety
Gonyaulax schilleri Matzenauer, 1933 · unaccepted (synonym)
Pyrodinium bahamense f. compressum Böhm, 1931 · unaccepted (basionym)
Pyrodinium schilleri (Matzenauer) Schiller · unaccepted (synonym)
marine
Not documented
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:41782
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:41782 [details]
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway (taxonomic information republished from AlgaeBase with permission of M.D. Guiry). Pyrodinium bahamense var. compressum (Böhm) Steidinger, Tester & F.J.R.Taylor, 1980. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=233399 on 2025-05-04
Date action by 2006-07-27 06:59:07Z created Camba Reu, Cibran 2015-06-26 12:00:51Z changed db_admin Copyright notice: the information originating from AlgaeBase may not be downloaded or replicated by any means, without the written permission of the copyright owner (generally AlgaeBase). Fair usage of data in scientific publications is permitted. Nomenclaturebasis of record
Gómez, F. (2005). A list of free-living dinoflagellate species in the world's oceans. <em>Acta Bot. Croat.</em> 64(1): 129-212. [details] new combination reference Steidinger K.A., Tester L.S. & Taylor F.J.R. 1980. A redescription of <i>Pyrodinium bahamense</i> var. <i>compressa</i> (Böhm) stat. nov. from Pacific red tides. Phycologia 19: 329-334. [details] Taxonomysource of synonymy
Mertens, K. N.; Wolny, J.; Carbonell-Moore, C.; Bogus, K.; Ellegaard, M.; Limoges, A.; De Vernal, A.; Gurdebeke, P.; Omura, T.; Al-Muftah, A.; Matsuoka, K. (2015). Taxonomic re-examination of the toxic armored dinoflagellate Pyrodinium bahamense Plate 1906: Can morphology or LSU sequencing separate P. bahamense var. compressum from var. bahamense?. <em>Harmful Algae.</em> 41: 1-24., available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2014.09.010 [details] source of synonymy Gómez, F. (2005). A list of free-living dinoflagellate species in the world's oceans. <em>Acta Bot. Croat.</em> 64(1): 129-212. [details] Otheradditional source
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. <em>World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway.</em> searched on YYYY-MM-DD., available online at http://www.algaebase.org [details]
additional source Tomas, C.R. (Ed.). (1997). Identifying marine phytoplankton. Academic Press: San Diego, CA [etc.] (USA). ISBN 0-12-693018-X. XV, 858 pp., available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/book/9780126930184 [details] additional source Harada T., Oshima Y., Kamiya H. & Yasumoto T. 1982. Confirmation of paralytic shellfish toxins in the dinoflagellate <i>Pyrodinium bahamense</i> var. <i>compressa</i> and bivalves in Palau. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 48: 821-825. [details] additional source Rosales-Loessener F., Porras E.D. & Dix M.W. 1989. Toxic shellfish poisoning in Guatemala. In: <i>Red Tides: Biology, Environmental Science, and Toxicology</i> (Ed. by T. Okaichi, D.M. Anderson & T. Nemoto), pp. 113-116. Elsevier, New York. [details] additional source Usup G., Kulis D.V. & Anderson D.M. 1995. Toxin production in a Malaysian isolate of the toxic dinoflagellate <i>Pyrodinium bahamense</i> var. <i>compressum</i>. In: <i>Harmful Marine Algal Blooms</i> (Ed. by P. Lassus, G. Arzul, E. Erard-Le Denn, P. Gentien, C. Marcaillou-Le Baut), pp. 519-524. Lavoisier, Paris. <br><br> Hummert C., Ritscher M., Reinhardt K. & Luckas B. 1997. Analysis of the characteristics PSP profiles of <i>Pyrodinium bahamense</i> and several strains of <i>Alexandrium</i> by HPLC based on ion-pair chromatographic separation, post-column oxidation, and fluorescence detection. Chromatographia 45: 312-316. [details] additional source Moestrup, Ø., Akselman, R., Cronberg, G., Elbraechter, M., Fraga, S., Halim, Y., Hansen, G., Hoppenrath, M., Larsen, J., Lundholm, N., Nguyen, L. N., Zingone, A. (Eds) (2009 onwards). IOC-UNESCO Taxonomic Reference List of Harmful Micro Algae., available online at http://www.marinespecies.org/HAB [details]  Present Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate Inaccurate  Introduced: alien Introduced: alien  Containing type locality Containing type locality
From editor or global species database
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:41782 [details]From regional or thematic species database
Harmful effect Producer of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins. [details]
Published in AlgaeBase
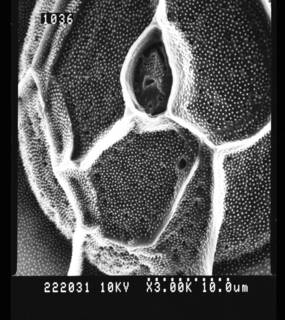
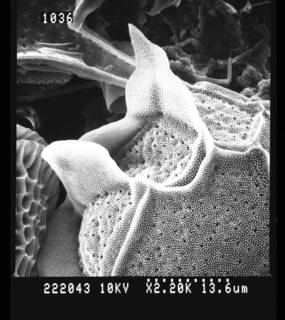
 Published in AlgaeBase  (from synonym Pyrodinium schilleri (Matzenauer) Schiller) (from synonym Pyrodinium schilleri (Matzenauer) Schiller)Published in AlgaeBase  (from synonym Gonyaulax schilleri Matzenauer, 1933) (from synonym Gonyaulax schilleri Matzenauer, 1933)Published in AlgaeBase  (from synonym Pyrodinium bahamense f. compressum Böhm, 1931) (from synonym Pyrodinium bahamense f. compressum Böhm, 1931)To Biodiversity Heritage Library (2 publications) To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Pyrodinium bahamense var. compressum) To GenBank (68212 nucleotides; 4 proteins) To GenBank (68212 nucleotides; 4 proteins) (from synonym Pyrodinium bahamense f. compressum Böhm, 1931) To NMNH Extant Collection (222031.jpg) To NMNH Extant Collection (222043.jpg) To ITIS |