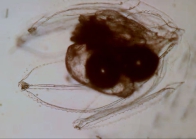
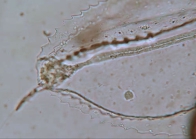
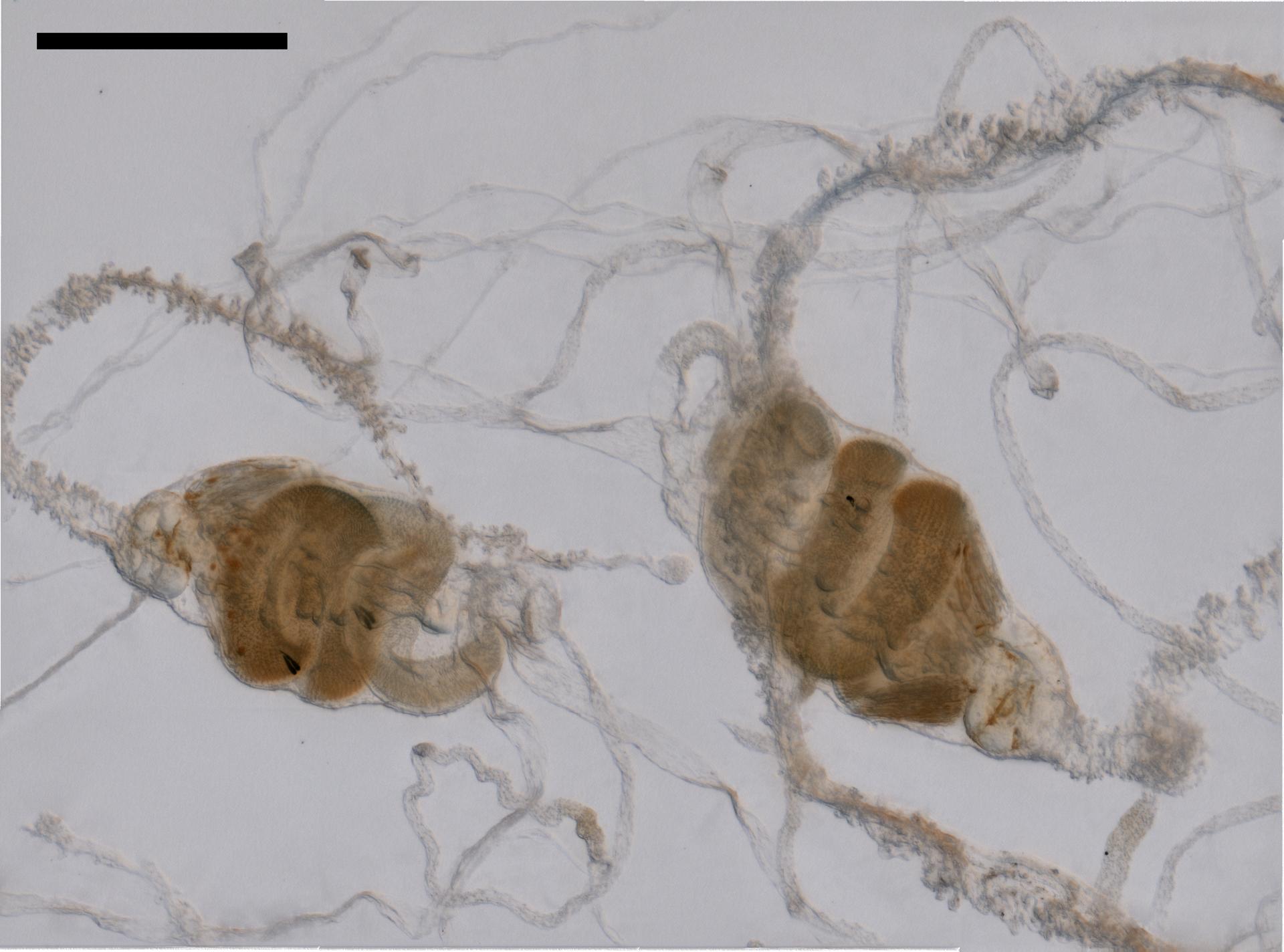
Hydrozoa taxon details
Agalma elegans (M. Sars, 1846)
135484 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:135484)
accepted
Species
Agalma sarsii (Kölliker, 1853) · unaccepted (unaccepted combination)
Agalmoides elegans (M. Sars, 1846) · unaccepted
Agalmopsis elegans M. Sars, 1846 · unaccepted (Basionym)
Agalmopsis Sarsii Kölliker, 1853 · unaccepted (Synonym)
Cuneolaria elegans (M. Sars, 1846) · unaccepted (unaccpted combination)
Cupulita sarsii (Kölliker, 1853) · unaccepted (unaccepted combination)
marine, brackish, fresh, terrestrial
recent only
(of Agalmopsis elegans M. Sars, 1846) Sars, M. (1846). Fauna littoralis Norvegiae oder Beschreibung und Abbildungen neuer oderwenig bekannter Seethiere, nebst Beobachtungen über die Organisation,Lebensweise und Entwickelung derselben. 1-194. Johann Dahk. Christiania., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/45526545
page(s): 36, pl. 5 figs 7, 8 (not 32-35, 37–41, pl. 5 figs 1-6 and pl. 6, = Nanomia cara) [details]
page(s): 36, pl. 5 figs 7, 8 (not 32-35, 37–41, pl. 5 figs 1-6 and pl. 6, = Nanomia cara) [details]
Depth range Deep-sea context derived from a specimen depth data search
Distribution This species is distributed in high abundances in the North-Atlantic ocean with a southern limit from Greenland, Iceland,...
Depth range Deep-sea context derived from a specimen depth data search [details]
Distribution This species is distributed in high abundances in the North-Atlantic ocean with a southern limit from Greenland, Iceland,...
Distribution This species is distributed in high abundances in the North-Atlantic ocean with a southern limit from Greenland, Iceland, Faroes, Shetlands and Hebrides. [details]
Schuchert, P. (2024). World Hydrozoa Database. Agalma elegans (M. Sars, 1846). Accessed at: https://www.marinespecies.org/hydrozoa/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=135484 on 2024-04-19
Date
action
by
original description
(of Agalmopsis Sarsii Kölliker, 1853) Kölliker, A. 1853. Die Schwimmpolypen oder Siphonophoren von Messina. Leipzig, Wilhelm Engelmann. Pp. 1-96, pls 12., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/12726286
page(s): 10 [details]
original description (of Agalmopsis elegans M. Sars, 1846) Sars, M. (1846). Fauna littoralis Norvegiae oder Beschreibung und Abbildungen neuer oderwenig bekannter Seethiere, nebst Beobachtungen über die Organisation,Lebensweise und Entwickelung derselben. 1-194. Johann Dahk. Christiania., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/45526545
page(s): 36, pl. 5 figs 7, 8 (not 32-35, 37–41, pl. 5 figs 1-6 and pl. 6, = Nanomia cara) [details]
context source (Deepsea) Sars, M. (1846). Fauna littoralis Norvegiae oder Beschreibung und Abbildungen neuer oderwenig bekannter Seethiere, nebst Beobachtungen über die Organisation,Lebensweise und Entwickelung derselben. 1-194. Johann Dahk. Christiania., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/45526545 [details]
context source (Bermuda) Moore, H.B. (1949). The zooplankton of the upper waters of the Bermuda area of the North Atlantic. Bulletin of the Bingham Oceanographic Collection 12(2):1-97, figs. 1-208. (i-1949) [details] Available for editors
context source (Hexacorallia) Fautin, Daphne G. (2013). Hexacorallians of the World. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Jacobs, W. 1937. Staatsquallen. Nat. Volk (Frank.) 67 (10): 465-473
page(s): 594 fig. 7c [details]
additional source Totton, A. K. 1955. Development and metamorphosis of the larva of Agalma elegans (Sars) (Siphonophora Physonectae). In “Papers in Marine Biology and Oceanography”. Edited by M. Graham. Deep-Sea Res. 3 (Suppl): 239-241.
page(s): 239, figs 1-9 [details]
additional source Cairns, S.D., L. Gershwin, F.J. Brook, P. Pugh, E.W. Dawson, O.V.; Ocaña, W. Vervoort, G. Williams, J.E. Watson, D.M. Opresko, P. Schuchert, P.M. Hine, D.P. Gordon, H.I. Campbell, A.J. Wright, J.A.Sánchez & D.G. Fautin. (2009). Phylum Cnidaria: corals, medusae, hydroids, myxozoans. <em>in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2009). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 1. Kingdom Animalia: Radiata, Lophotrochozoa, Deuterostomia.</em> pp. 59-101., available online at https://repository.si.edu/handle/10088/8431 [details] Available for editors
additional source Trott, T. J. (2004). Cobscook Bay inventory: a historical checklist of marine invertebrates spanning 162 years. <em>Northeastern Naturalist.</em> 11, 261-324., available online at http://www.gulfofmaine.org/kb/files/9793/TROTT-Cobscook%20List.pdf [details] Available for editors
additional source Calder, D. (2003). Checklist of Hydroids, hydromedusae and siphonophores reported from the Bay of Fundy. [details]
additional source Linkletter, L. E. (1977). A checklist of marine fauna and flora of the Bay of Fundy. <em>Huntsman Marine Laboratory, St. Andrews, N.B.</em> 68: p. [details]
additional source Bigelow, H. B. (1911). The Siphonophorae. Reports of the scientific research expedition to the tropical Pacific. Albatross XXIII. <em>Memoirs of the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard College.</em> 38: 173-401, 32 pls., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/32451
page(s): 281, pl.18 figs 9-13, pl.19 figs 1-4 [details]
additional source Pugh, P. R. (1999). Siphonophorae. In South Atlantic Zooplankton I. Edited by D. Boltovskoy. <em>Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, The Netherlands.</em> 1-868.
page(s): 481 figs 3.6, 3.22 [details]
additional source Totton, A. K. (1954). Siphonophora of the Indian Ocean together with systematic and biological notes on related specimens from other oceans. <em>Discovery Rep.</em> 27: 1-162., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/5611213
page(s): 61 fig. 24 + frontispiece [details]
additional source Shih, C.T., 1977. A guide to the Jellyfish of Canadian Atlantic waters. National Museum of Natural Sciences, Natural History Series 5 : 1-190. [details]
additional source Fewkes J.W. (1881b). Studies of the Jelly-fishes of Narragansett Bay. <em>Bulletin of the Museum of comparative Zoölogy of Harvard College.</em> 8: 141-182, pls 1-10., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/28861419
page(s): 163 pl. 9 figs 1-21, pl.10 [details]
additional source Dunn, C. W.; Pugh, P. R.; Haddock, S. H. D. (2005). Molecular phylogenetics of the Siphonophora (Cnidaria), with implications for the evolution of functional specialisation. <em>Syst. Biol.</em> 54(6): 916-935.
page(s): 922, figs 2b, 4a-b, 5, 6, 7, 8a-b [details]
additional source Pugh, P. R. & Gasca, R. (2009). Siphonophorae (Cnidaria) of the Gulf of Mexico. Pp. 395–402. In: Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. <em>Biodiversity.</em> Texas A&M Press, College Station, Texas. [details]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
ecology source Kawamura, T. 1911c. “Shidarezakura Kurage” and “Nagayoraku Kurage” (Cupulita picta, Metschnikoff, and Agalmopsis elegans, Sars). Zool. Mag. (Tokyo) (Dobuts. Zhasshi) 23 (7): 359-363, plate 7 (In Japanese). [details]
page(s): 10 [details]
original description (of Agalmopsis elegans M. Sars, 1846) Sars, M. (1846). Fauna littoralis Norvegiae oder Beschreibung und Abbildungen neuer oderwenig bekannter Seethiere, nebst Beobachtungen über die Organisation,Lebensweise und Entwickelung derselben. 1-194. Johann Dahk. Christiania., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/45526545
page(s): 36, pl. 5 figs 7, 8 (not 32-35, 37–41, pl. 5 figs 1-6 and pl. 6, = Nanomia cara) [details]
context source (Deepsea) Sars, M. (1846). Fauna littoralis Norvegiae oder Beschreibung und Abbildungen neuer oderwenig bekannter Seethiere, nebst Beobachtungen über die Organisation,Lebensweise und Entwickelung derselben. 1-194. Johann Dahk. Christiania., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/45526545 [details]
context source (Bermuda) Moore, H.B. (1949). The zooplankton of the upper waters of the Bermuda area of the North Atlantic. Bulletin of the Bingham Oceanographic Collection 12(2):1-97, figs. 1-208. (i-1949) [details] Available for editors
context source (Hexacorallia) Fautin, Daphne G. (2013). Hexacorallians of the World. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Jacobs, W. 1937. Staatsquallen. Nat. Volk (Frank.) 67 (10): 465-473
page(s): 594 fig. 7c [details]
additional source Totton, A. K. 1955. Development and metamorphosis of the larva of Agalma elegans (Sars) (Siphonophora Physonectae). In “Papers in Marine Biology and Oceanography”. Edited by M. Graham. Deep-Sea Res. 3 (Suppl): 239-241.
page(s): 239, figs 1-9 [details]
additional source Cairns, S.D., L. Gershwin, F.J. Brook, P. Pugh, E.W. Dawson, O.V.; Ocaña, W. Vervoort, G. Williams, J.E. Watson, D.M. Opresko, P. Schuchert, P.M. Hine, D.P. Gordon, H.I. Campbell, A.J. Wright, J.A.Sánchez & D.G. Fautin. (2009). Phylum Cnidaria: corals, medusae, hydroids, myxozoans. <em>in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2009). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 1. Kingdom Animalia: Radiata, Lophotrochozoa, Deuterostomia.</em> pp. 59-101., available online at https://repository.si.edu/handle/10088/8431 [details] Available for editors
additional source Trott, T. J. (2004). Cobscook Bay inventory: a historical checklist of marine invertebrates spanning 162 years. <em>Northeastern Naturalist.</em> 11, 261-324., available online at http://www.gulfofmaine.org/kb/files/9793/TROTT-Cobscook%20List.pdf [details] Available for editors
additional source Calder, D. (2003). Checklist of Hydroids, hydromedusae and siphonophores reported from the Bay of Fundy. [details]
additional source Linkletter, L. E. (1977). A checklist of marine fauna and flora of the Bay of Fundy. <em>Huntsman Marine Laboratory, St. Andrews, N.B.</em> 68: p. [details]
additional source Bigelow, H. B. (1911). The Siphonophorae. Reports of the scientific research expedition to the tropical Pacific. Albatross XXIII. <em>Memoirs of the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard College.</em> 38: 173-401, 32 pls., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/32451
page(s): 281, pl.18 figs 9-13, pl.19 figs 1-4 [details]
additional source Pugh, P. R. (1999). Siphonophorae. In South Atlantic Zooplankton I. Edited by D. Boltovskoy. <em>Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, The Netherlands.</em> 1-868.
page(s): 481 figs 3.6, 3.22 [details]
additional source Totton, A. K. (1954). Siphonophora of the Indian Ocean together with systematic and biological notes on related specimens from other oceans. <em>Discovery Rep.</em> 27: 1-162., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/5611213
page(s): 61 fig. 24 + frontispiece [details]
additional source Shih, C.T., 1977. A guide to the Jellyfish of Canadian Atlantic waters. National Museum of Natural Sciences, Natural History Series 5 : 1-190. [details]
additional source Fewkes J.W. (1881b). Studies of the Jelly-fishes of Narragansett Bay. <em>Bulletin of the Museum of comparative Zoölogy of Harvard College.</em> 8: 141-182, pls 1-10., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/28861419
page(s): 163 pl. 9 figs 1-21, pl.10 [details]
additional source Dunn, C. W.; Pugh, P. R.; Haddock, S. H. D. (2005). Molecular phylogenetics of the Siphonophora (Cnidaria), with implications for the evolution of functional specialisation. <em>Syst. Biol.</em> 54(6): 916-935.
page(s): 922, figs 2b, 4a-b, 5, 6, 7, 8a-b [details]
additional source Pugh, P. R. & Gasca, R. (2009). Siphonophorae (Cnidaria) of the Gulf of Mexico. Pp. 395–402. In: Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. <em>Biodiversity.</em> Texas A&M Press, College Station, Texas. [details]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
ecology source Kawamura, T. 1911c. “Shidarezakura Kurage” and “Nagayoraku Kurage” (Cupulita picta, Metschnikoff, and Agalmopsis elegans, Sars). Zool. Mag. (Tokyo) (Dobuts. Zhasshi) 23 (7): 359-363, plate 7 (In Japanese). [details]
 Present
Present  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
From editor or global species database
Depth range Deep-sea context derived from a specimen depth data search [details]From other sources
Distribution This species is distributed in high abundances in the North-Atlantic ocean with a southern limit from Greenland, Iceland, Faroes, Shetlands and Hebrides. [details]
To Barcode of Life (13 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (12 publications) (from synonym Agalma sarsii (Kölliker, 1853))
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (46 publications)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (63 publications) (from synonym Agalmopsis elegans M. Sars, 1846)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (8 publications) (from synonym Agalmopsis Sarsii Kölliker, 1853)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (8 publications) (from synonym Cupulita sarsii (Kölliker, 1853))
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL)
To European Nucleotide Archive (ENA)
To GenBank (13 nucleotides; 7 proteins)
To GenBank (13 nucleotides; 7 proteins) (from synonym Agalmopsis elegans M. Sars, 1846)
To Global Biotic Interactions (GloBI)
To PESI
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (1 record) (from synonym Agalma sarsii (Kölliker, 1853))
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (34 records)
To Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History (YPM IZ 106655)
To ITIS
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (12 publications) (from synonym Agalma sarsii (Kölliker, 1853))
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (46 publications)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (63 publications) (from synonym Agalmopsis elegans M. Sars, 1846)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (8 publications) (from synonym Agalmopsis Sarsii Kölliker, 1853)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (8 publications) (from synonym Cupulita sarsii (Kölliker, 1853))
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL)
To European Nucleotide Archive (ENA)
To GenBank (13 nucleotides; 7 proteins)
To GenBank (13 nucleotides; 7 proteins) (from synonym Agalmopsis elegans M. Sars, 1846)
To Global Biotic Interactions (GloBI)
To PESI
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (1 record) (from synonym Agalma sarsii (Kölliker, 1853))
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (34 records)
To Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History (YPM IZ 106655)
To ITIS