Difference between revisions of "Temperature sensors"
(→Calibration) |
|||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
<ref>http://www.rdfcorp.com/anotes/pa-rtd/pa-rtd_01.shtml</ref> | <ref>http://www.rdfcorp.com/anotes/pa-rtd/pa-rtd_01.shtml</ref> | ||
===Thermistors=== | ===Thermistors=== | ||
| + | [[Image: thermistor.jpg| thumb| 400px|left|Examples of Thermistors]] | ||
Thermistors are temperature sensitive resistors. The principle behind the functioning of this sensor is much like the one from the RTD, however thermistors differ from RTDs in that the material used in a thermistor is generally a ceramic or polymer, while RTDs use pure metals and, also unlike RTDs, the resistance of a thermistor decreases with increasing temperature. The temperature response is different as well; RTDs are useful over broader temperature ranges, while thermistors typically achieve a higher precision within a limited temperature range, usually −90 °C to 130 °C. | Thermistors are temperature sensitive resistors. The principle behind the functioning of this sensor is much like the one from the RTD, however thermistors differ from RTDs in that the material used in a thermistor is generally a ceramic or polymer, while RTDs use pure metals and, also unlike RTDs, the resistance of a thermistor decreases with increasing temperature. The temperature response is different as well; RTDs are useful over broader temperature ranges, while thermistors typically achieve a higher precision within a limited temperature range, usually −90 °C to 130 °C. | ||
<ref>http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/mastascu/elessonshtml/Sensors/TempR.html</ref> | <ref>http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/mastascu/elessonshtml/Sensors/TempR.html</ref> | ||
Revision as of 12:21, 12 July 2012
Contents

|

|
The authors below are planning to work on this article
See also: Instruments and sensors to measure environmental parameters
Introduction
Temperature Definition
Temperature is a difficult concept to define. Ordinarily, temperature is a qualitative measure for classifying how matter appears to be hot or cold. More specifically, matter is made up of moving particles (molecules), each molecule has its own motion speed, the kinetic energy. Temperature is a physical parameter that describes the average kinetic energy of molecules, it is not a measure of energy itself, but it is proportional to the average kinetic energy of molecules. That means that the hotter molecules are, the more they move and the higher is the temperature. By contrast, when molecules do not move at all, i.e., their kinetic energy is zero, so the temperature is 0ºK (absolute zero, -273.15ºC) [1]
Sensors
| Type | Thermometric Variable |
|---|---|
| liquid in glass | volume |
| constant volume gas | pressure |
| bimetallic strip | coil pitch |
| electric resistor | resistance |
| thermocouple | voltage |
| Different types of thermometers and respective
thermometric variables | |
A thermometer is an instrument that measures temperature. However, it is impossible to measure the kinetic state of molecules directly, instead, thermometers measure parameters that vary proportionally with the kinetic state of molecules, called the thermometric variables; thus, there are several different techniques to measure temperature depending on the thermometric variable. The most commonly used temperature sensors in oceanography are the Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) and the Thermistors. [2][3]
Temperature Scales
Temperature scales are based on “temperature standard points”, points at which a phenomenon occurs at constant temperature. Fahrenheit scale was developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit (in 1724) supposedly based on the lowest temperature achieved at the time (0ºF) and using 180 degrees between the freezing and the boiling point of water, 32 ºF and 212 ºF, respectively. As seen above, Kelvin scale (K) is based on the absolute zero with 100 degrees between the freezing and the boiling point of water. The zero value of the Celsius scale is based on the freezing point of water and the degree range is the same as in Kelvin. SI units are represented in Kelvin (K), while the most commonly used scale is Celsius. [4]
RTDs
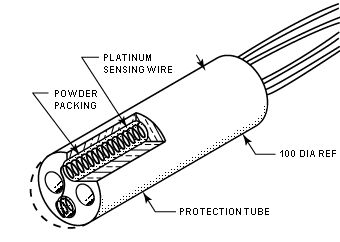
The principle behind this sensor is that of that pure metals change their resistivity with temperature in a predictable way. RTDs are constructed with metals whose resistivity increases linearly with temperature. Metals used should a have high boiling point, be easily available in its pure form, be resistant to corrosion (chemical stability) and electrical properties that are highly reproducible. The most commonly used metal is platinum but copper and nickel are also used. [5]
Thermistors
Thermistors are temperature sensitive resistors. The principle behind the functioning of this sensor is much like the one from the RTD, however thermistors differ from RTDs in that the material used in a thermistor is generally a ceramic or polymer, while RTDs use pure metals and, also unlike RTDs, the resistance of a thermistor decreases with increasing temperature. The temperature response is different as well; RTDs are useful over broader temperature ranges, while thermistors typically achieve a higher precision within a limited temperature range, usually −90 °C to 130 °C. [6] [7]
Thermocouples
Thermocouples are based on the Seebeck effect: two dissimilar metals bearing different temperatures, joint together at at least two different points (a reference and a measuring point) will produce electromotive force proportional to the temperature. Different metal-pairs produce different outputs (i.e., temperature ranges). Thermocouples are not as accurate as thermistors or RTDs but can take readings of very high temperatures ranges over 2000°C). They are used, for instance, in High Temperature Probes attached to ROVs exploring hydrothermal vents. [8] [9]
Calibration
Calibration is necessary to verify the sensor/instrument performance and to ensure that the sensor maintains its performance over time. RTDs and thermistors are calibrated by generating Temperature vs. Resistance graphs and then comparing them with international standard (IPTS-68, ITS-90), thermocouples are calibrated similarly by building a calibration graph with voltage and temperature while measuring the reference temperature with an accurate thermometer or using a “temperature standard point”. Since the actual sensor cannot be calibrated the calibration is done on the signal output. [10] [11]
Examples of Instruments:
CTD - thermistors / RTDs T chain - thermistors XBT - thermistors HT probes - thermocouples
See also
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Resistance_thermometer http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thermistor
References
- ↑ http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/thermo/temper2.html
- ↑ http://physics.info/temperature/
- ↑ http://www.o-vations.com/marinetech/physicalsensors.html
- ↑ http://abyss.uoregon.edu/~js/glossary/temperature_scale.html
- ↑ http://www.rdfcorp.com/anotes/pa-rtd/pa-rtd_01.shtml
- ↑ http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/mastascu/elessonshtml/Sensors/TempR.html
- ↑ http://www.technologystudent.com/elec1/therm1.htm
- ↑ http://www.picotech.com/applications/thermocouple.html
- ↑ http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/mastascu/elessonshtml/Sensors/TempThermCpl.html
- ↑ http://www.burnsengineering.com/document/papers/calibration-why_when_how_handout.pdf
- ↑ http://www.davis.com/TechLibraryArticle/1225