Copepoda name details
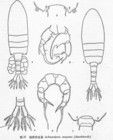
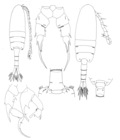
Pseudodiaptomus inopinus Burckhardt, 1913
361260 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:361260)
alternative representation
Species
Schmackeria inopinus (Burckhardt, 1913) · unaccepted (synonym)
marine, brackish, fresh, terrestrial
Burckhardt, G. (1913). Wissenschaftliche Ergebnisse einer Reise um die Erde von M. Pernod und C. Schröter. III. Zooplankton aus ost- und süd-asiatischen Binnengewässern. Zoologische Jahrbücher, Abteilung für Systematik, Ökologie und Geographie der Tiere 34(4):341-472, pls. 9-17. (15-v-1913) [details] 
Walter, T.C.; Boxshall, G. (2024). World of Copepods Database. Pseudodiaptomus inopinus Burckhardt, 1913. Accessed at: https://www.marinespecies.org/copepoda/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=361260 on 2024-04-23
Date
action
by
original description
Burckhardt, G. (1913). Wissenschaftliche Ergebnisse einer Reise um die Erde von M. Pernod und C. Schröter. III. Zooplankton aus ost- und süd-asiatischen Binnengewässern. Zoologische Jahrbücher, Abteilung für Systematik, Ökologie und Geographie der Tiere 34(4):341-472, pls. 9-17. (15-v-1913) [details] 
context source (Introduced species) Molnar, J.L., R.L. Gamboa, C. Revenga & M.D. Spalding. (2008). Assessing the global threat of invasive species to marine biodiversity. <em>Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment.</em> 6(9): 485-492., available online at https://www.conservationgateway.org/ConservationPractices/Marine/Pages/marineinvasives.aspx [details] Available for editors
basis of record Walter, T. Chad. The World of Copepods. International online database. , available online at http://www.marinespecies.org/copepoda [details]
additional source Shen, C.J., A.Y. Tai, C.Z. Zhang, Z.Y. Li, D.X. Song, Y.Z. Song & G.X. Chen. (1979). Crustacea: Freshwater Copepoda. <em>Fauna Sinica (unnumbered), Academia Sinica Research Group of Carcinology Institute of Zoology, Science Press, Peking, China.</em> 450 pp. [in Chinese]. [details] Available for editors
additional source Chang, C.Y. (2009). Illustrated encyclopedia of fauna & flora of Korea. Vol. 42. Inland-water Copepoda. Jeonghaeng-sa, Ministry of Education, Seoul, South Korea 687 pp. [details] Available for editors
additional source Sakaguchi, S.O. & H. Ueda. (2010). A new species of Pseudodiaptomus (Copepoda: Calanoida) from Japan, with notes on the closely related P. inopinus Burckhardt, 1913 from Kyushu Island. <em>Zootaxa.</em> 2623:52-68. [details] Available for editors
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Park, E.O., J.R. Cordell & H.Y. Soh. (2013). Occurrence characteristics of two sibling species, Pseudodiaptomus inopinus and Pseudodiaptomus poplesia (Copepoda, Calanoida, Pseudodiaptomidae), in the Mankyung River estuary, South Korea. Zoological Studies 52, available online at https://doi.org/10.1186/1810-522X-52-7 [details] Available for editors
additional source Cordell, J.R. & S.M. Morrison. (1996). The invasive Asian copepod Pseudodiaptomus inopinus in Oregon, Washington, and British Columbia estuaries. Estuaries 19(3):629-638. [details] Available for editors
additional source Cordell, J.R., C.A. Morgan & C.A. Simenstad. (1992). Occurrence of the Asian calanoid copepod Pseudodiaptomus inopinus in the zooplankton of the Columbia River Estuary. Journal of Crustacean Biology 12(2):260-269. [details] Available for editors
additional source Cordell, J.R., M. Rasmussen & S.M. Bollens. (2007). Biology of the introduced copepod Pseudodiaptomus inopinus in a Northeast Pacific estuary. Marine Ecology Progress Series 333:213-227. [details] Available for editors
additional source Dussart, B.H. & D. Defaye. (2001). Copepoda: Introduction to the Copepoda. (2nd edition)(revised and enlarged). <em>Guides to the Identification of the Microinvertebrates of the Continental Waters of the World. H.J.F. Dumont (ed.). SPB Academic Publishers, The Hague.</em> 16:1-344. [details] Available for editors
additional source Eyun, S.I., Y.H. Lee, H.L. Suh, S. Kim & H.Y. Soh. (2007). Genetic identification and molecular phylogeny of Pseudodiaptomus species (Calanoida, Pseudodiaptomidae) in Korean waters. Zoological Science 24(3):265-271. [details] Available for editors
additional source Kos, M.S. (1985). K faune Calanoida (Copepoda) pribrezhnykh raonov Yuzhnogo Sakhalina. On the fauna of Calanoida (Copepoda) off coasts of South Sakhalin. <em>In: Golikov, A.N. (ed.). Biotsenozy i fauna shel'fa yuzhnogo Sakhalina. Biocoenoses and fauna of the shelf of South Sakhalin. Issledovaniya Fauny Morei.</em> 30(38):225-258, figs. 1-17. (for 1984, Russian with English summary). [details] Available for editors
additional source Oka, S.I., T. Saisho & R. Hirota. (1991). Pseudodiaptomus (Crustacea, Copepoda) in the brackish waters of mangrove regions in the Nansei Islands, southwestern Japan. Bulletin of the Biogeographical Society of Japan 46(8):83-88, figs. 1-4.
page(s): 85 [details] Available for editors
additional source Smirnov, S.S. (1929). Beiträge zur Copepodenfauna Ostasiens. Zoologischer Anzeiger 81(11-12):317-329, figs. 1-9. (15-v-1929) [details] Available for editors
additional source Kasyan, V.V. (2017). First Record of Copepod Pseudodiaptomus inopinus Burckhardt, 1913 in Peter the Great Bay, Sea of Japan. Obnaruzheniye kopepody Pseudodiaptomus inopinus Burckhardt, 1913 v zalive petra velikogo yaponskogo morya. <em>Russian Journal of Biological Invasions, Rossiskii Zhurnal Biologicheskikh Invazii.</em> 8(2):131-134. [Original Russian Text © V.V. Kasyan, 2017, published in Rossiiskii Zhurnal Biologicheskikh Invazii, 2017, No. 1, pp. 20–24.]. [details] Available for editors
additional source Dexter, E., S.M. Bollens, J.R. Cordell, H.Y. Soh, G. Rollwagen-Bollens, S.P. Pfeifer, J. Goudet & S. Vuilleumier. (2018). A genetic reconstruction of the invasion of the calanoid copepod Pseudodiaptomus inopinus across the North American Pacific Coast. <em>Biological Invasions.</em> 20(6):1577-1595., available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-017-1649-0 [details] Available for editors
additional source Sakaguchi, S.O. & H. Ueda. (2018). Genetic analysis on Pseudodiaptomus inopinus (Copepoda, Calanoida) species complex in Japan: revival of the species name of P. japonicus Kikuchi, 1928. Plankton & Benthos Research, 13(4):173-179., available online at https://doi.org/10.3800/pbr.13.173 [details] Available for editors
additional source Chae, Y.J., H.J. Oh, K.H. Chang, I.S. Kwak & H. Jo. (2021). Application of Next-Generation Sequencing for the Determination of the Bacterial Community in the Gut Contents of Brackish Copepod Species (Acartia hudsonica, Sinocalanus tenellus, and Pseudodiaptomus inopinus). <em>Animals.</em> 11(2):1-14. Feb 2021., available online at https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11020542 [details] Available for editors
additional source Matsui, H., T. Sasaki, T. Kobari, V. Waqalevu, K. Kikuchi, M. Ishikawa & T. Kotani. (2021). DHA Accumulation in the Polar Lipids of the Euryhaline Copepod Pseudodiaptomus inopinus and Its Transfer to Red Sea Bream Pagrus major Larvae. <em>Frontiers In Marine Science.</em> 8:1-15. Feb 2021., available online at https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2021.632876 [details] Available for editors
additional source Morrison, S.M. (1994). A study of the introducd asian calanoid copepod Pseudiaptomus inopinus. <em>Thesis, University of Puget Sound, Seattle Washington.</em> 40 pp. [details] Available for editors
additional source Sasaki, T., H. Matsui, Y. Kuwabara, S. Yokoyama, M. Ishikawa & T. Kotani. (2024). Euryhaline copepod Pseudodiaptomus inopinus changed the prey preference of red sea bream Pagrus major larvae. <em>Fisheries Science.</em> 9(1): Jan 2024., available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-024-01751-8 [details]
source of synonymy Walter, T.C., S. Ohtsuka & L.V. Castillo. (2006). A new species of Pseudodiaptomus (Crustacea: Copepoda: Calanoida) from the Philippines, with a key to pseudodiaptomids from the Philippines and comments on the status of the genus Schmackeria. Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington 119(2):202-221. [details] Available for editors
ecology source Brun, P., M.R. Payne & T. Kiørboe. (2017). A trait database for marine copepods. <em>Earth System Science Data.</em> 9(1):99-113., available online at https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-9-99-2017 [details] Available for editors
context source (Introduced species) Molnar, J.L., R.L. Gamboa, C. Revenga & M.D. Spalding. (2008). Assessing the global threat of invasive species to marine biodiversity. <em>Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment.</em> 6(9): 485-492., available online at https://www.conservationgateway.org/ConservationPractices/Marine/Pages/marineinvasives.aspx [details] Available for editors
basis of record Walter, T. Chad. The World of Copepods. International online database. , available online at http://www.marinespecies.org/copepoda [details]
additional source Shen, C.J., A.Y. Tai, C.Z. Zhang, Z.Y. Li, D.X. Song, Y.Z. Song & G.X. Chen. (1979). Crustacea: Freshwater Copepoda. <em>Fauna Sinica (unnumbered), Academia Sinica Research Group of Carcinology Institute of Zoology, Science Press, Peking, China.</em> 450 pp. [in Chinese]. [details] Available for editors
additional source Chang, C.Y. (2009). Illustrated encyclopedia of fauna & flora of Korea. Vol. 42. Inland-water Copepoda. Jeonghaeng-sa, Ministry of Education, Seoul, South Korea 687 pp. [details] Available for editors
additional source Sakaguchi, S.O. & H. Ueda. (2010). A new species of Pseudodiaptomus (Copepoda: Calanoida) from Japan, with notes on the closely related P. inopinus Burckhardt, 1913 from Kyushu Island. <em>Zootaxa.</em> 2623:52-68. [details] Available for editors
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Park, E.O., J.R. Cordell & H.Y. Soh. (2013). Occurrence characteristics of two sibling species, Pseudodiaptomus inopinus and Pseudodiaptomus poplesia (Copepoda, Calanoida, Pseudodiaptomidae), in the Mankyung River estuary, South Korea. Zoological Studies 52, available online at https://doi.org/10.1186/1810-522X-52-7 [details] Available for editors
additional source Cordell, J.R. & S.M. Morrison. (1996). The invasive Asian copepod Pseudodiaptomus inopinus in Oregon, Washington, and British Columbia estuaries. Estuaries 19(3):629-638. [details] Available for editors
additional source Cordell, J.R., C.A. Morgan & C.A. Simenstad. (1992). Occurrence of the Asian calanoid copepod Pseudodiaptomus inopinus in the zooplankton of the Columbia River Estuary. Journal of Crustacean Biology 12(2):260-269. [details] Available for editors
additional source Cordell, J.R., M. Rasmussen & S.M. Bollens. (2007). Biology of the introduced copepod Pseudodiaptomus inopinus in a Northeast Pacific estuary. Marine Ecology Progress Series 333:213-227. [details] Available for editors
additional source Dussart, B.H. & D. Defaye. (2001). Copepoda: Introduction to the Copepoda. (2nd edition)(revised and enlarged). <em>Guides to the Identification of the Microinvertebrates of the Continental Waters of the World. H.J.F. Dumont (ed.). SPB Academic Publishers, The Hague.</em> 16:1-344. [details] Available for editors
additional source Eyun, S.I., Y.H. Lee, H.L. Suh, S. Kim & H.Y. Soh. (2007). Genetic identification and molecular phylogeny of Pseudodiaptomus species (Calanoida, Pseudodiaptomidae) in Korean waters. Zoological Science 24(3):265-271. [details] Available for editors
additional source Kos, M.S. (1985). K faune Calanoida (Copepoda) pribrezhnykh raonov Yuzhnogo Sakhalina. On the fauna of Calanoida (Copepoda) off coasts of South Sakhalin. <em>In: Golikov, A.N. (ed.). Biotsenozy i fauna shel'fa yuzhnogo Sakhalina. Biocoenoses and fauna of the shelf of South Sakhalin. Issledovaniya Fauny Morei.</em> 30(38):225-258, figs. 1-17. (for 1984, Russian with English summary). [details] Available for editors
additional source Oka, S.I., T. Saisho & R. Hirota. (1991). Pseudodiaptomus (Crustacea, Copepoda) in the brackish waters of mangrove regions in the Nansei Islands, southwestern Japan. Bulletin of the Biogeographical Society of Japan 46(8):83-88, figs. 1-4.
page(s): 85 [details] Available for editors
additional source Smirnov, S.S. (1929). Beiträge zur Copepodenfauna Ostasiens. Zoologischer Anzeiger 81(11-12):317-329, figs. 1-9. (15-v-1929) [details] Available for editors
additional source Kasyan, V.V. (2017). First Record of Copepod Pseudodiaptomus inopinus Burckhardt, 1913 in Peter the Great Bay, Sea of Japan. Obnaruzheniye kopepody Pseudodiaptomus inopinus Burckhardt, 1913 v zalive petra velikogo yaponskogo morya. <em>Russian Journal of Biological Invasions, Rossiskii Zhurnal Biologicheskikh Invazii.</em> 8(2):131-134. [Original Russian Text © V.V. Kasyan, 2017, published in Rossiiskii Zhurnal Biologicheskikh Invazii, 2017, No. 1, pp. 20–24.]. [details] Available for editors
additional source Dexter, E., S.M. Bollens, J.R. Cordell, H.Y. Soh, G. Rollwagen-Bollens, S.P. Pfeifer, J. Goudet & S. Vuilleumier. (2018). A genetic reconstruction of the invasion of the calanoid copepod Pseudodiaptomus inopinus across the North American Pacific Coast. <em>Biological Invasions.</em> 20(6):1577-1595., available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-017-1649-0 [details] Available for editors
additional source Sakaguchi, S.O. & H. Ueda. (2018). Genetic analysis on Pseudodiaptomus inopinus (Copepoda, Calanoida) species complex in Japan: revival of the species name of P. japonicus Kikuchi, 1928. Plankton & Benthos Research, 13(4):173-179., available online at https://doi.org/10.3800/pbr.13.173 [details] Available for editors
additional source Chae, Y.J., H.J. Oh, K.H. Chang, I.S. Kwak & H. Jo. (2021). Application of Next-Generation Sequencing for the Determination of the Bacterial Community in the Gut Contents of Brackish Copepod Species (Acartia hudsonica, Sinocalanus tenellus, and Pseudodiaptomus inopinus). <em>Animals.</em> 11(2):1-14. Feb 2021., available online at https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11020542 [details] Available for editors
additional source Matsui, H., T. Sasaki, T. Kobari, V. Waqalevu, K. Kikuchi, M. Ishikawa & T. Kotani. (2021). DHA Accumulation in the Polar Lipids of the Euryhaline Copepod Pseudodiaptomus inopinus and Its Transfer to Red Sea Bream Pagrus major Larvae. <em>Frontiers In Marine Science.</em> 8:1-15. Feb 2021., available online at https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2021.632876 [details] Available for editors
additional source Morrison, S.M. (1994). A study of the introducd asian calanoid copepod Pseudiaptomus inopinus. <em>Thesis, University of Puget Sound, Seattle Washington.</em> 40 pp. [details] Available for editors
additional source Sasaki, T., H. Matsui, Y. Kuwabara, S. Yokoyama, M. Ishikawa & T. Kotani. (2024). Euryhaline copepod Pseudodiaptomus inopinus changed the prey preference of red sea bream Pagrus major larvae. <em>Fisheries Science.</em> 9(1): Jan 2024., available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-024-01751-8 [details]
source of synonymy Walter, T.C., S. Ohtsuka & L.V. Castillo. (2006). A new species of Pseudodiaptomus (Crustacea: Copepoda: Calanoida) from the Philippines, with a key to pseudodiaptomids from the Philippines and comments on the status of the genus Schmackeria. Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington 119(2):202-221. [details] Available for editors
ecology source Brun, P., M.R. Payne & T. Kiørboe. (2017). A trait database for marine copepods. <em>Earth System Science Data.</em> 9(1):99-113., available online at https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-9-99-2017 [details] Available for editors
 Present
Present  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
From regional or thematic species database
Introduced species impact in United States part of the North Pacific Ocean (Marine Region) : Outcompetes native species for resources and/or space [details]Introduced species vector dispersal United States part of the North Pacific Ocean (Marine Region) Ships: accidental with ballast water, sea water systems, live wells or other deck basins [details]
Marine Planktonic Copepods (Banyuls/OOB/UPMC/CNRS) Note: Including taxonomic identification plates, remarks, geographic distribution, ecological information & reference list
To Barcode of Life (7 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (1 publication) (from synonym Schmackeria inopinus (Burckhardt, 1913))
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (5 publications)
To European Nucleotide Archive (ENA)
To GenBank (14 nucleotides; 8 proteins)
To GenBank (14 nucleotides; 8 proteins) (from synonym Schmackeria inopinus (Burckhardt, 1913))
To Global Invasive Species Database (GISD)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Arthropoda Collection (10 records)
US FISH WILDLIFE page
To ITIS
To Barcode of Life (7 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (1 publication) (from synonym Schmackeria inopinus (Burckhardt, 1913))
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (5 publications)
To European Nucleotide Archive (ENA)
To GenBank (14 nucleotides; 8 proteins)
To GenBank (14 nucleotides; 8 proteins) (from synonym Schmackeria inopinus (Burckhardt, 1913))
To Global Invasive Species Database (GISD)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Arthropoda Collection (10 records)
US FISH WILDLIFE page
To ITIS