WoRMS taxon details
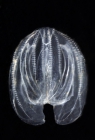
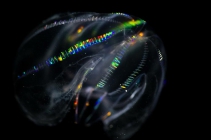
Mnemiopsis leidyi A. Agassiz, 1865
106401 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:106401)
accepted
Species
Alcinoe rosea Mertens, 1833 · unaccepted
Alcinoe vermicularis Rang, 1828 · unaccepted > misspelling
Alcinoe vermiculata Rang, 1828 · unaccepted
Mnemia schweiggeri Eschscholtz, 1825 · unaccepted
Mnemiopsis mccradyi Mayer, 1900 · unaccepted (junior synonym)
marine, brackish, fresh, terrestrial
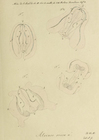
Agassiz, A. (1865). North American Acalephae. <em>Illustrated Catalogue of the Museum of Comparative Zoölogy at Harvard College.</em> 2: 1-234., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/bibliography/1837
page(s): 20-23, figs. 22-24 [details]
page(s): 20-23, figs. 22-24 [details]
Note Naushon, Buzzard's Bay
Type locality Naushon, Buzzard's Bay
[details]
[details]
Distribution Virginian, southside of Cape Cod to Cape Hatteras
Distribution Virginian, southside of Cape Cod to Cape Hatteras [details]
Mills, C.E. Internet (1998-present). Phylum Ctenophora: list of all valid species names. Electronic internet document. Mnemiopsis leidyi A. Agassiz, 1865. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=106401 on 2024-04-18
Date
action
by
2006-09-20 08:42:16Z
changed
Martinez, Olga
![]() The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License
The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License
original description
Agassiz, A. (1865). North American Acalephae. <em>Illustrated Catalogue of the Museum of Comparative Zoölogy at Harvard College.</em> 2: 1-234., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/bibliography/1837
page(s): 20-23, figs. 22-24 [details]
original description (of Alcinoe rosea Mertens, 1833) Mertens, H. (1833). Beobachtungen und Untersuchungen über die Beroëartigen Akalephen. <em>Mémoires de l'Académie impériale des sciences de St.-Pétersbourg. 6e série, Sciences mathématiques, physiques et naturelles.</em> 479-543. 13 plates., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/55630086
page(s): 507, pl. 4, figs. 1-4 [details]
original description (of Alcinoe vermicularis Rang, 1828) Rang, S. (1828). Établissement de la famille des Béroïdes dans l'ordre des acalèphes libres, et description de deux genres nouveaux qui lui appartiennent. <em>Mémoires de la Société d'Histoire Naturelle de Paris 4: 166-173, pls. 119-120.</em>
page(s): 168-169, pl. 19, figs. 1-4 [details]
original description (of Mnemiopsis mccradyi Mayer, 1900) Mayer, A. G. 1900. Descriptions of new and little-known medusae from the western Atlantic. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology of Harvard 37: 1-9, plates 1-6., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/4271637
page(s): 9, pl. 6, figs. 22-23 [details]
original description (of Mnemia schweiggeri Eschscholtz, 1825) Eschscholtz, Johann Friedrich von. (1825). Bericht über die zoologische Ausbeute während der Reise von Kronstadt bis St. Peter und Paul. <em>Isis von Oken.</em> 1825(6): 733-747, plate V., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/27509188
page(s): 741 [details]
original description (of Alcinoe vermiculata Rang, 1828) Rang, S. (1828). Établissement de la famille des Béroïdes dans l'ordre des acalèphes libres, et description de deux genres nouveaux qui lui appartiennent. <em>Mémoires de la Société d'Histoire Naturelle de Paris 4: 166-173, pls. 119-120.</em>
page(s): 168-169, pl. 19, figs. 1-4 [details]
context source (Introduced species) Katsanevakis, S.; Bogucarskis, K.; Gatto, F.; Vandekerkhove, J.; Deriu, I.; Cardoso A.S. (2012). Building the European Alien Species Information Network (EASIN): a novel approach for the exploration of distributed alien species data. <em>BioInvasions Records.</em> 1: 235-245., available online at http://easin.jrc.ec.europa.eu [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
context source (Schelde) (2010). Bedreiging voor biodiversiteit. Indicatoren voor het Schelde-estuarium. <em>Opgemaakt in opdracht van Afdeling Maritieme Toegang, projectgroep EcoWaMorSe, Vlaams Nederlandse Scheldecommissie. VLIZ Information Sheets, 200. Vlaams Instituut voor de Zee (VLIZ): Oostende.</em> 7 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details]
context source (BeRMS 2020) Bio-environmental research group; Institute of Agricultural and Fisheries research (ILVO), Belgium; (2015): Zooplankton monitoring in the Belgian Part of the North Sea between 2009 and 2010. [details]
context source (Bermuda) Sterrer, W. (1986). Marine fauna and flora of Bermuda: a systematic guide to the identification of marine organisms. <em>Wiley-Interscience Publication. Wiley.</em> 742 pp (Nemertini part). [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
basis of record van der Land, J. (2001). Ctenophora. <em>in: Costello, M.J. et al. (Ed.) (2001). European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification.</em> Collection Patrimoines Naturels 50: pp. 122-123. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Pollock, L.W. (1998). A practical guide to the marine animals of northeastern North America. Rutgers University Press. New Brunswick, New Jersey & London. 367 pp., available online at http://books.google.com/books?id=i1AmT31cuR4C [details]
additional source Streftaris, N., A. Zenetos & E. Papathanassiou. (2005). Globalisation in marine ecosystems: the story of non-indigenous marine species across European seas. <em>Oceanogry and Marine Biology: an Annual Review.</em> 43: 419-453. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Savini, D.; Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A. (2006). Consumption rates and prey preference of the invasive gastropod Rapana venosa in the Northern Adriatic Sea. Helgol. Mar. Res. 60(2): 153-159. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Zenetos, A.; Çinar, M.E.; Pancucci-Papadopoulou, M.A.; Harmelin, J.-G.; Furnari, G.; Andaloro, F.; Bellou, N.; Streftaris, N.; Zibrowius, H. (2005). Annotated list of marine alien species in the Mediterranean with records of the worst invasive species. <em>Mediterranean Marine Science.</em> 6 (2): 63-118., available online at https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273213810_Annotated_list_of_marine_alien_species_in_the_Mediterranean_with_records_of_the_worst_invasive_species [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Moss, A. G. 2009. Ctenophora of the Gulf of Mexico, Pp. 403–411 in Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. Biodiversity. Texas A&M Press, College Station, Texas. [details]
additional source Mills, C. E. (1998-present). Phylum Ctenophora: list of all valid species names. [Internet]., available online at http://faculty.washington.edu/cemills/Ctenolist.html [details]
additional source Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A., A. Marchini, G. Cantone, A. Castelli, C. Chimenz, M. Cormaci, C. Froglia, G. Furnari, M.C. Gambi, G. Giaccone, A. Giangrande, C. Gravil, F. Mastrototaro, C. Mazziotti, L. Orsi-Relini & S. Piraino. (2010). Alien species along the Italian coasts: an overview. <em>Biological Invasions.</em> 13(1): 215-237., available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-010-9803-y [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Zenetos, A.; Gofas, S.; Verlaque, M.; Cinar, M.; Garcia Raso, J.; Bianchi, C.; Morri, C.; Azzurro, E.; Bilecenoglu, M.; Froglia, C.; Siokou, I.; Violanti, D.; Sfriso, A.; San Martin, G.; Giangrande, A.; Katagan, T.; Ballesteros, E.; Ramos-Espla, A.; Mastrototaro, F.; Ocana, O.; Zingone, A.; Gambi, M.; Streftaris, N. (2010). Alien species in the Mediterranean Sea by 2010. A contribution to the application of European Union's Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). Part I. Spatial distribution. <em>Mediterranean Marine Science.</em> 11(2): 381-493., available online at https://doi.org/10.12681/mms.87 [details]
additional source van der Land, J. (ed). (2008). UNESCO-IOC Register of Marine Organisms (URMO). , available online at http://www.marinespecies.org/urmo/ [details]
page(s): 20-23, figs. 22-24 [details]
original description (of Alcinoe rosea Mertens, 1833) Mertens, H. (1833). Beobachtungen und Untersuchungen über die Beroëartigen Akalephen. <em>Mémoires de l'Académie impériale des sciences de St.-Pétersbourg. 6e série, Sciences mathématiques, physiques et naturelles.</em> 479-543. 13 plates., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/55630086
page(s): 507, pl. 4, figs. 1-4 [details]
original description (of Alcinoe vermicularis Rang, 1828) Rang, S. (1828). Établissement de la famille des Béroïdes dans l'ordre des acalèphes libres, et description de deux genres nouveaux qui lui appartiennent. <em>Mémoires de la Société d'Histoire Naturelle de Paris 4: 166-173, pls. 119-120.</em>
page(s): 168-169, pl. 19, figs. 1-4 [details]
original description (of Mnemiopsis mccradyi Mayer, 1900) Mayer, A. G. 1900. Descriptions of new and little-known medusae from the western Atlantic. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology of Harvard 37: 1-9, plates 1-6., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/4271637
page(s): 9, pl. 6, figs. 22-23 [details]
original description (of Mnemia schweiggeri Eschscholtz, 1825) Eschscholtz, Johann Friedrich von. (1825). Bericht über die zoologische Ausbeute während der Reise von Kronstadt bis St. Peter und Paul. <em>Isis von Oken.</em> 1825(6): 733-747, plate V., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/27509188
page(s): 741 [details]
original description (of Alcinoe vermiculata Rang, 1828) Rang, S. (1828). Établissement de la famille des Béroïdes dans l'ordre des acalèphes libres, et description de deux genres nouveaux qui lui appartiennent. <em>Mémoires de la Société d'Histoire Naturelle de Paris 4: 166-173, pls. 119-120.</em>
page(s): 168-169, pl. 19, figs. 1-4 [details]
context source (Introduced species) Katsanevakis, S.; Bogucarskis, K.; Gatto, F.; Vandekerkhove, J.; Deriu, I.; Cardoso A.S. (2012). Building the European Alien Species Information Network (EASIN): a novel approach for the exploration of distributed alien species data. <em>BioInvasions Records.</em> 1: 235-245., available online at http://easin.jrc.ec.europa.eu [details] Available for editors
context source (Schelde) (2010). Bedreiging voor biodiversiteit. Indicatoren voor het Schelde-estuarium. <em>Opgemaakt in opdracht van Afdeling Maritieme Toegang, projectgroep EcoWaMorSe, Vlaams Nederlandse Scheldecommissie. VLIZ Information Sheets, 200. Vlaams Instituut voor de Zee (VLIZ): Oostende.</em> 7 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details]
context source (BeRMS 2020) Bio-environmental research group; Institute of Agricultural and Fisheries research (ILVO), Belgium; (2015): Zooplankton monitoring in the Belgian Part of the North Sea between 2009 and 2010. [details]
context source (Bermuda) Sterrer, W. (1986). Marine fauna and flora of Bermuda: a systematic guide to the identification of marine organisms. <em>Wiley-Interscience Publication. Wiley.</em> 742 pp (Nemertini part). [details] Available for editors
basis of record van der Land, J. (2001). Ctenophora. <em>in: Costello, M.J. et al. (Ed.) (2001). European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification.</em> Collection Patrimoines Naturels 50: pp. 122-123. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Pollock, L.W. (1998). A practical guide to the marine animals of northeastern North America. Rutgers University Press. New Brunswick, New Jersey & London. 367 pp., available online at http://books.google.com/books?id=i1AmT31cuR4C [details]
additional source Streftaris, N., A. Zenetos & E. Papathanassiou. (2005). Globalisation in marine ecosystems: the story of non-indigenous marine species across European seas. <em>Oceanogry and Marine Biology: an Annual Review.</em> 43: 419-453. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Savini, D.; Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A. (2006). Consumption rates and prey preference of the invasive gastropod Rapana venosa in the Northern Adriatic Sea. Helgol. Mar. Res. 60(2): 153-159. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Zenetos, A.; Çinar, M.E.; Pancucci-Papadopoulou, M.A.; Harmelin, J.-G.; Furnari, G.; Andaloro, F.; Bellou, N.; Streftaris, N.; Zibrowius, H. (2005). Annotated list of marine alien species in the Mediterranean with records of the worst invasive species. <em>Mediterranean Marine Science.</em> 6 (2): 63-118., available online at https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273213810_Annotated_list_of_marine_alien_species_in_the_Mediterranean_with_records_of_the_worst_invasive_species [details] Available for editors
additional source Moss, A. G. 2009. Ctenophora of the Gulf of Mexico, Pp. 403–411 in Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. Biodiversity. Texas A&M Press, College Station, Texas. [details]
additional source Mills, C. E. (1998-present). Phylum Ctenophora: list of all valid species names. [Internet]., available online at http://faculty.washington.edu/cemills/Ctenolist.html [details]
additional source Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A., A. Marchini, G. Cantone, A. Castelli, C. Chimenz, M. Cormaci, C. Froglia, G. Furnari, M.C. Gambi, G. Giaccone, A. Giangrande, C. Gravil, F. Mastrototaro, C. Mazziotti, L. Orsi-Relini & S. Piraino. (2010). Alien species along the Italian coasts: an overview. <em>Biological Invasions.</em> 13(1): 215-237., available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-010-9803-y [details] Available for editors
additional source Zenetos, A.; Gofas, S.; Verlaque, M.; Cinar, M.; Garcia Raso, J.; Bianchi, C.; Morri, C.; Azzurro, E.; Bilecenoglu, M.; Froglia, C.; Siokou, I.; Violanti, D.; Sfriso, A.; San Martin, G.; Giangrande, A.; Katagan, T.; Ballesteros, E.; Ramos-Espla, A.; Mastrototaro, F.; Ocana, O.; Zingone, A.; Gambi, M.; Streftaris, N. (2010). Alien species in the Mediterranean Sea by 2010. A contribution to the application of European Union's Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). Part I. Spatial distribution. <em>Mediterranean Marine Science.</em> 11(2): 381-493., available online at https://doi.org/10.12681/mms.87 [details]
additional source van der Land, J. (ed). (2008). UNESCO-IOC Register of Marine Organisms (URMO). , available online at http://www.marinespecies.org/urmo/ [details]
 Present
Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio
Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
From editor or global species database
Type locality Naushon, Buzzard's Bay[details]
From regional or thematic species database
Introduced species abundance in Israeli part of the Mediterranean Sea - Eastern Basin (Marine Region) : Common [details]Introduced species abundance in Baltic Sea (IHO Sea Area) : Common [details]
Introduced species abundance in Spanish part of the Mediterranean Sea - Western Basin (Marine Region) : Locally common [details]
Introduced species abundance in Israeli part of the Mediterranean Sea - Eastern Basin (Marine Region) : Common [details]
Introduced species abundance in Baltic Sea (IHO Sea Area) : Locally common [details]
Introduced species abundance in Danish part of the Kattegat (Marine Region) : Common [details]
Introduced species impact in Israeli part of the Mediterranean Sea - Eastern Basin (Marine Region) : Alters trophic interactions [details]
Introduced species impact in Baltic Sea (IHO Sea Area) : Consumes native species (predator or herbivore) [details]
Introduced species impact in Belgian part of the North Sea (Marine Region) : Consumes native species (predator or herbivore) [details]
Introduced species impact in Spanish part of the Mediterranean Sea - Western Basin (Marine Region) : Loss of aquaculture/commercial/recreational harvest or gain [details]
Introduced species impact in Ukraine (Nation) : Other impact - undefined or uncertain [details]
Introduced species impact in Israeli part of the Mediterranean Sea - Eastern Basin (Marine Region) : Loss of aquaculture/commercial/recreational harvest or gain [details]
Introduced species impact in Baltic Sea (IHO Sea Area) : Consumes native species (predator or herbivore) [details]
Introduced species impact in Aegean Sea (IHO Sea Area) : Alters trophic interactions [details]
Introduced species impact in Black Sea (IHO Sea Area) : Alters trophic interactions [details]
Introduced species impact in Belgian part of the North Sea (Marine Region) : Outcompetes native species for resources and/or space [details]
Introduced species impact German part of the North Sea (Marine Region) Consumes native species (predator or herbivore) [details]
Introduced species population trend in Belgian part of the North Sea (Marine Region) : Increasing [details]
Introduced species remark in Baltic Sea (IHO Sea Area) : Despite the low present predation impact by M. leidyi on zooplankton, the ctenophore may exert a significant predatory influence on Baltic cod eggs at relatively low abundances due to an overlap in their vertical distribution in the Bornholm Basin. [details]
Introduced species remark In Israeli part of the Mediterranean Sea - Eastern Basin (Marine Region) : Swarms of the species pose a threat to local coastal power and desalination plants. Plant engineers were forced to increase the frequency of backwash cycles in the pretreatment stage and consequently increasing the discharge of coagulants such as ferric s [details]
Introduced species remark In Baltic Sea (IHO Sea Area) : High potential for explosive population development and negative influences on fish stocks [details]
Introduced species remark In Slovenian part of the Adriatic Sea (Marine Region) : After the first record in 2005 of a swarm of M. leidyi the species was not reported again in the Gulf of Trieste or other areas of the Adriatic Sea (Lipej et al. 2012) [details]
Introduced species vector dispersal in Israeli part of the Mediterranean Sea - Eastern Basin (Marine Region) : Ships: accidental with ballast water, sea water systems, live wells or other deck basins [details]
Introduced species vector dispersal in Belgian part of the North Sea (Marine Region) : Ships: accidental with ballast water, sea water systems, live wells or other deck basins [details]
Introduced species vector dispersal in Israeli part of the Mediterranean Sea - Eastern Basin (Marine Region) : Ships: accidental with ballast water, sea water systems, live wells or other deck basins [details]
Introduced species vector dispersal in Baltic Sea (IHO Sea Area) : Ships: accidental with ballast water, sea water systems, live wells or other deck basins [details]
Introduced species vector dispersal in Slovenian part of the Adriatic Sea (Marine Region) : Ships: accidental with ballast water, sea water systems, live wells or other deck basins [details]
Introduced species vector dispersal in Ukraine (Nation) : Shipping [details]
Introduced species vector dispersal in Belgian part of the North Sea: Ships: accidental with ballast water, sea water systems, live wells or other deck basins [details]
From other sources
Alien species The sea walnut Mnemiopsis leidyi is an infamous predator of zooplankton and fish eggs. The species’ natural area of distribution is along the Atlantic coast of North- and South-America. In the 1980's the sea walnut was accidently introduced in the Black Sea as a stowaway in ballast water of cargo ships. The introduction led to a collapse of the ecosystem. Since a couple of years, the sea walnut is also present in the North Sea, and we now have to wait and see what ecological consequences it will bring to the region. [details]Distribution Virginian, southside of Cape Cod to Cape Hatteras [details]
Remark Introduced in Belgium since 2007. [details]
| Language | Name | |
|---|---|---|
| Danish | dræbergopleAmerikansk ribbegople | [details] |
| Dutch | Leidy's ribkwalAmerikaanse ribkwalAmerikaanse langlob-ribkwal | [details] |
| English | warty comb jellysea walnutcat's eyeAmerican comb jelly | [details] |
| Finnish | amerikankampamaneetti | [details] |
| French | cténophore américain | [details] |
| German | MeerwalnussMeereswallnussKatzenauge | [details] |
| Italian | noce di mare | [details] |
| Swedish | amerikansk kammanet | [details] |
European Network on Invasive Alien Species (NOBANIS) - Mnemiopsis leidyi
Global invasive species database - Mnemiopsis leidyi
PlanktonNet Image
To Barcode of Life (6 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (10 publications) (from synonym Alcinoe rosea Mertens, 1833)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (10 publications) (from synonym Mnemiopsis mccradyi Mayer, 1900)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (86 publications)
To European Nucleotide Archive (ENA)
To GenBank (46152 nucleotides; 358 proteins)
To GenBank (46152 nucleotides; 358 proteins) (from synonym Mnemiopsis mccradyi Mayer, 1900)
To Global Biotic Interactions (GloBI)
To Global Invasive Species Database (GISD)
To Information system on Aquatic Non-Indigenous and Cryptogenic Species (AquaNIS)
To Niet-inheemse soorten Belgisch deel Noordzee en aanpalende estuaria (in Dutch)
To PESI
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Ctenophora Collection (10 records)
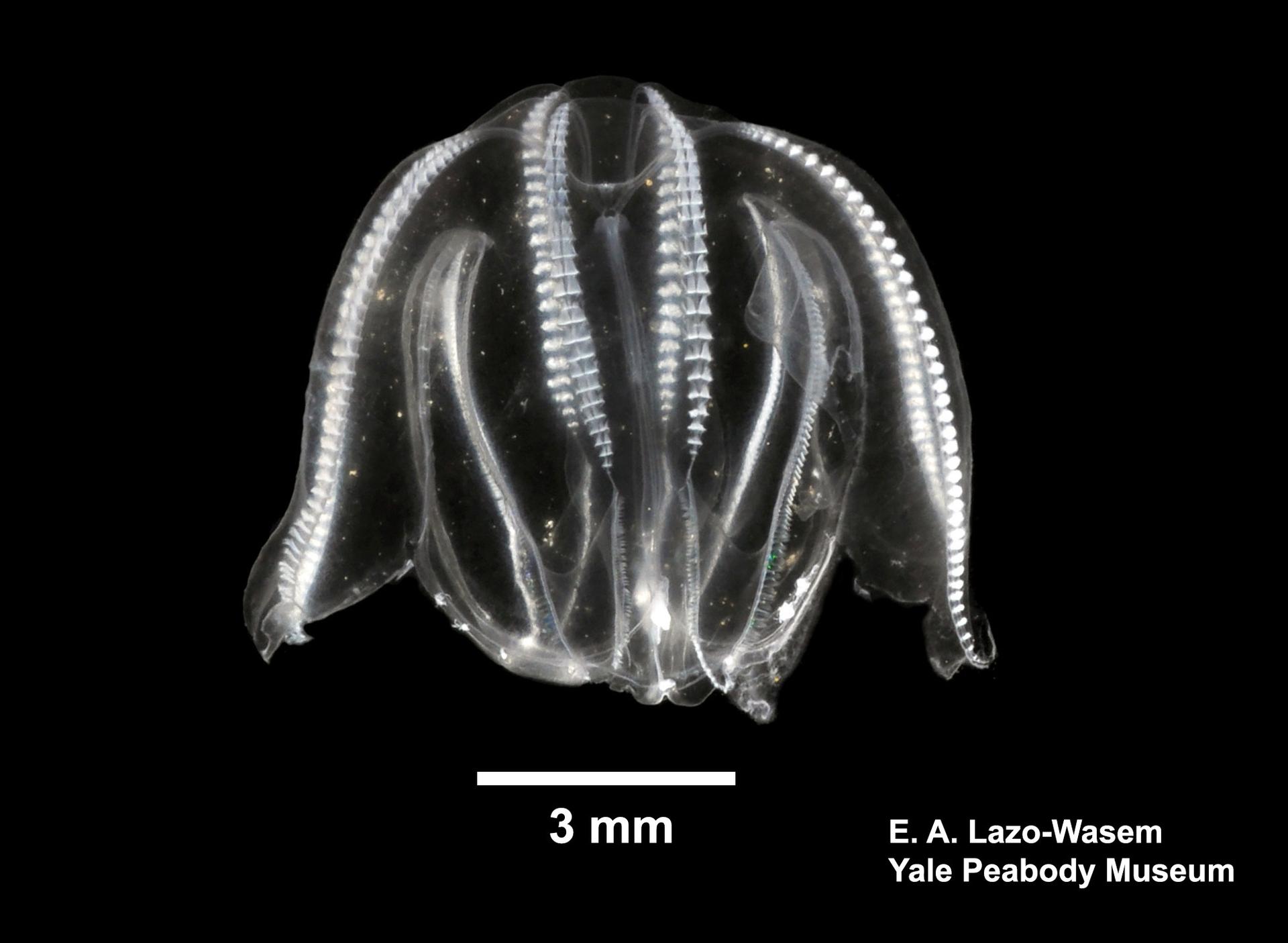
To Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History (YPM IZ 101232)
To ITIS
Global invasive species database - Mnemiopsis leidyi
PlanktonNet Image
To Barcode of Life (6 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (10 publications) (from synonym Alcinoe rosea Mertens, 1833)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (10 publications) (from synonym Mnemiopsis mccradyi Mayer, 1900)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (86 publications)
To European Nucleotide Archive (ENA)
To GenBank (46152 nucleotides; 358 proteins)
To GenBank (46152 nucleotides; 358 proteins) (from synonym Mnemiopsis mccradyi Mayer, 1900)
To Global Biotic Interactions (GloBI)
To Global Invasive Species Database (GISD)
To Information system on Aquatic Non-Indigenous and Cryptogenic Species (AquaNIS)
To Niet-inheemse soorten Belgisch deel Noordzee en aanpalende estuaria (in Dutch)
To PESI
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Ctenophora Collection (10 records)
To Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History (YPM IZ 101232)
To ITIS