WoRMS taxon details
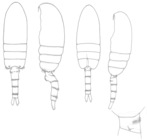
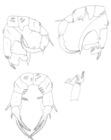
Pseudodiaptomus forbesi (Poppe & Richard, 1890)
355153 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:355153)
accepted
Species
Schmackeria forbesi Poppe & Richard, 1890 · unaccepted (synonym)
marine, brackish, fresh, terrestrial
(of Schmackeria forbesi Poppe & Richard, 1890) Poppe, S.A. & J. Richard. (1890). Description du Schmackeria forbesi n. gen. et sp., Calanide nouveau recueilli par M. Schmacker dans les eaux douces des environs de Shanghai. Mémoires de la Société Zoologique de France 3(5):396-403, pl. 10.
page(s): 396 [details]
page(s): 396 [details]
Walter, T.C.; Boxshall, G. (2024). World of Copepods Database. Pseudodiaptomus forbesi (Poppe & Richard, 1890). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=355153 on 2024-04-23
Date
action
by
![]() The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License
The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License
original description
(of Schmackeria forbesi Poppe & Richard, 1890) Poppe, S.A. & J. Richard. (1890). Description du Schmackeria forbesi n. gen. et sp., Calanide nouveau recueilli par M. Schmacker dans les eaux douces des environs de Shanghai. Mémoires de la Société Zoologique de France 3(5):396-403, pl. 10.
page(s): 396 [details]
basis of record Walter, T. Chad. The World of Copepods. International online database. , available online at http://www.marinespecies.org/copepoda [details]
additional source Shen, C.J., A.Y. Tai, C.Z. Zhang, Z.Y. Li, D.X. Song, Y.Z. Song & G.X. Chen. (1979). Crustacea: Freshwater Copepoda. <em>Fauna Sinica (unnumbered), Academia Sinica Research Group of Carcinology Institute of Zoology, Science Press, Peking, China.</em> 450 pp. [in Chinese].
page(s): :67-69, fig.26 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Burckhardt, G. (1913). Wissenschaftliche Ergebnisse einer Reise um die Erde von M. Pernod und C. Schröter. III. Zooplankton aus ost- und süd-asiatischen Binnengewässern. Zoologische Jahrbücher, Abteilung für Systematik, Ökologie und Geographie der Tiere 34(4):341-472, pls. 9-17. (15-v-1913)
note: :379-394, pl.11-12 [details]
additional source Kikuchi, K. (1928). Freshwater Calanoida of middle and south-western Japan. Memoirs of the College of Sciences, Kyoto Imperial University, Series B 4(1, article 3):65-79, pls. 18-22.
page(s): :69-70, pl.19, fig.19-20 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Kimmerer, W.J., J.R. Burau & W.A. Bennett. (1998). Tidally oriented vertical migration and position maintenance of zooplankton in a temperate estuary. Limnology and Oceanography 43(7):1697-1709. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Marsh, C.D. (1933). Synopsis of the calanoid crustaceans, exclusive of the Diaptomidae, found in fresh and brackish waters, chiefly of North America. Proceedings of the United States National Museum 82(18)(2959):1-58, pls. 1-24. (30-vi-1933)
page(s): :44, pl.21, fig.4-7 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Mashiko, K. (1951). Studies of the fresh-water plankton of central China, II. Scientific Reports, Kanazawa Unviersity 1(2):137-154. (vi-1951).
page(s): :151, fig.6e-h [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Mashiko, K. (1951). Studies on the fresh-water plankton of Central China, I. Scientific Reports, Kanazawa Unviersity 1(1): 17-31, figs. 1-3, tabs. 1-5. (iii-1951).
page(s): :18-21 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Mashiko, K. (1954). On the geographical distribution of some brackish and freshwater copepods in and around Japan. Scientific Reports, Kanazawa Unviersity 2(2):35-41. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Mashiko, K. (1955). A study of the brackish-water plankton in Japan, with special reference to the relation between the plankton fauna and the salinity of the water. Scientific Reports, Kanazawa University 4(1): 135-150, fig. 1.
page(s): :140-141 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Mashiko, K. & A. Inoue. (1952). Limnological studies of the brackish-water lakes in the Hokuriku District, Japan. Special Publication of the Japan Sea Regional Fisheries Research Laboratory, 3rd Anniversary of Its Founding :175-191, figs. 1-9.
page(s): :184-185, fig.8f-k [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Richard, J. (1891). Recherches sur le systeme glandulaire et sur le systeme nerveux des copepodes libres d'eau douce. Theses Presentées à la Faculté des Sciences de Paris, Série A 169:113-270, pl. 5-8.(we have partial translation only )
page(s): :140, fig.5; note: nervous system [details]
additional source Shen, C.J. & A.Y. Tai. (1962). The Copepoda of the Wu-Li Lake, Wu-Sih, Kiangsu Province. I. Calanoida. Acta Zoologica Sinica 14(1):99-118, figs. 1-34. (iii-1962, Chinese with English summary). [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Shen, C.J. & A.Y. Tai. (1962). The Copepoda of the Wu-Li Lake, Wu-Sih, Kiangsu Province. III. Harpacticoida. <em>Acta Zoologica Sinica.</em> 14(3):393-410, figs. 1-53. (ix-1962, Chinese with English summary). (Vide: Communist China Science Abstr., 51: 13. (1970)).
page(s): :403, 406 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Shen, C.J. & F.S. Lee. (1963). The estuarine Copepoda of Chiekong and Zaikong Rivers, Kwantung Province, China. Acta Zoologica Sinica 15(4):571-596. (xii-1996, Chinese with English summary).
page(s): :577 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Breckenridge, J.K. , S.M. Bollens & G. Rollwagen-Bollens. (2014). Plankton assemblage variability in a river-dominated temperate estuary during late spring (high-flow) and late summer (low-flow) periods. <em>Estuaries and Coasts.</em> 38(1):93-103. [online May 2014]., available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-014-9820-7 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Emerson, J.E., S.M. Bollens & T.D. Counihan. (2015). Seasonal dynamics of zooplankton in Columbia-Snake River reservoirs, with special emphasis on the invasive copepod Pseudodiaptomus forbesi. Aquatic Invasions, 10(1):25-40., available online at https://doi.org/10.3391/ai.2015.10.1.03 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Bowen, A., G. Rollwagen-Bollens, S.M. Bollens & J. Zimmerman. (2015). Feeding of the invasive copepod Pseudodiaptomus forbesi on natural microplankton assemblages within the lower Columbia River. Journal Of Plankton Research, 37(6):1089-1094., available online at https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbv078 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Borutzky, E.V. (1960). Opredelitel' svobodnozhivushchikh presnovodnykh veslonogikh rakov SSSR i sopredel'nykh stran po fragmentam v kishechnikakh ryb. (Key for determining the free-living freshwater Copepoda of the USSR and neighboring countries, from fragments in fish stomachs. <em>Akademiya Nauk SSSR, Moscow.</em> 1-217, figs. 1-77.
page(s): :22, fig.4-5 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Gearty, A.J., T.R. Ignoffo, A.M. Slaughter & W.J. Kimmerer. (2021). Growth and reproductive rates of the dominant copepod Pseudodiaptomus forbesi in response to environmental factors and habitat type in the northern San Francisco Estuary. <em>Aquatic Ecology.</em> 55(3):1-25. MAY 2021., available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-021-09863-4 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Yelton, R. A.M. Slaugher & W.J. Kimmerer. (2022). Diel Behaviors of Zooplankton Interact with Tidal Patterns to Drive Spatial Subsidies in the Northern San Francisco Estuary. <em>Estuaries and Coasts.</em> , available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-021-01036-8 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Gearty, A.J. (2020). Mechanisms controlling productivity of a calanoid copepod in northern San Francisco estuary. <em>M.Sc. Thesis, San Francisco State University, San Francisco, California, USA.</em> 45 pp., available online at https://doi.org/10.46569/20.500.12680/s1784r547 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Hartman, R. (2019). 24 Hour Bugs: Tidal and diel changes in zooplankton distribution in the Sacramento River. <em>Interagency Ecological Program for the San Francisco Estuary. IEP Newsletter.</em> 34(1):11-22., available online at https://nrm.dfg.ca.gov/FileHandler.ashx?DocumentID=184974 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Kayfetz, K.R. (2014). Biotic vs. abiotic effects on distribution of the estuarine copepod Pseudodiaptomus forbesi. <em>M.Sc. Thesis, San Francisco State University, San Francisco, California, USA.</em> , available online at http://hdl.handle.net/10211.3/131290 [details]
ecology source Brun, P., M.R. Payne & T. Kiørboe. (2017). A trait database for marine copepods. <em>Earth System Science Data.</em> 9(1):99-113., available online at https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-9-99-2017 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
page(s): 396 [details]
basis of record Walter, T. Chad. The World of Copepods. International online database. , available online at http://www.marinespecies.org/copepoda [details]
additional source Shen, C.J., A.Y. Tai, C.Z. Zhang, Z.Y. Li, D.X. Song, Y.Z. Song & G.X. Chen. (1979). Crustacea: Freshwater Copepoda. <em>Fauna Sinica (unnumbered), Academia Sinica Research Group of Carcinology Institute of Zoology, Science Press, Peking, China.</em> 450 pp. [in Chinese].
page(s): :67-69, fig.26 [details] Available for editors
additional source Burckhardt, G. (1913). Wissenschaftliche Ergebnisse einer Reise um die Erde von M. Pernod und C. Schröter. III. Zooplankton aus ost- und süd-asiatischen Binnengewässern. Zoologische Jahrbücher, Abteilung für Systematik, Ökologie und Geographie der Tiere 34(4):341-472, pls. 9-17. (15-v-1913)
note: :379-394, pl.11-12 [details]
additional source Kikuchi, K. (1928). Freshwater Calanoida of middle and south-western Japan. Memoirs of the College of Sciences, Kyoto Imperial University, Series B 4(1, article 3):65-79, pls. 18-22.
page(s): :69-70, pl.19, fig.19-20 [details] Available for editors
additional source Kimmerer, W.J., J.R. Burau & W.A. Bennett. (1998). Tidally oriented vertical migration and position maintenance of zooplankton in a temperate estuary. Limnology and Oceanography 43(7):1697-1709. [details] Available for editors
additional source Marsh, C.D. (1933). Synopsis of the calanoid crustaceans, exclusive of the Diaptomidae, found in fresh and brackish waters, chiefly of North America. Proceedings of the United States National Museum 82(18)(2959):1-58, pls. 1-24. (30-vi-1933)
page(s): :44, pl.21, fig.4-7 [details] Available for editors
additional source Mashiko, K. (1951). Studies of the fresh-water plankton of central China, II. Scientific Reports, Kanazawa Unviersity 1(2):137-154. (vi-1951).
page(s): :151, fig.6e-h [details] Available for editors
additional source Mashiko, K. (1951). Studies on the fresh-water plankton of Central China, I. Scientific Reports, Kanazawa Unviersity 1(1): 17-31, figs. 1-3, tabs. 1-5. (iii-1951).
page(s): :18-21 [details] Available for editors
additional source Mashiko, K. (1954). On the geographical distribution of some brackish and freshwater copepods in and around Japan. Scientific Reports, Kanazawa Unviersity 2(2):35-41. [details] Available for editors
additional source Mashiko, K. (1955). A study of the brackish-water plankton in Japan, with special reference to the relation between the plankton fauna and the salinity of the water. Scientific Reports, Kanazawa University 4(1): 135-150, fig. 1.
page(s): :140-141 [details] Available for editors
additional source Mashiko, K. & A. Inoue. (1952). Limnological studies of the brackish-water lakes in the Hokuriku District, Japan. Special Publication of the Japan Sea Regional Fisheries Research Laboratory, 3rd Anniversary of Its Founding :175-191, figs. 1-9.
page(s): :184-185, fig.8f-k [details] Available for editors
additional source Richard, J. (1891). Recherches sur le systeme glandulaire et sur le systeme nerveux des copepodes libres d'eau douce. Theses Presentées à la Faculté des Sciences de Paris, Série A 169:113-270, pl. 5-8.(we have partial translation only )
page(s): :140, fig.5; note: nervous system [details]
additional source Shen, C.J. & A.Y. Tai. (1962). The Copepoda of the Wu-Li Lake, Wu-Sih, Kiangsu Province. I. Calanoida. Acta Zoologica Sinica 14(1):99-118, figs. 1-34. (iii-1962, Chinese with English summary). [details] Available for editors
additional source Shen, C.J. & A.Y. Tai. (1962). The Copepoda of the Wu-Li Lake, Wu-Sih, Kiangsu Province. III. Harpacticoida. <em>Acta Zoologica Sinica.</em> 14(3):393-410, figs. 1-53. (ix-1962, Chinese with English summary). (Vide: Communist China Science Abstr., 51: 13. (1970)).
page(s): :403, 406 [details] Available for editors
additional source Shen, C.J. & F.S. Lee. (1963). The estuarine Copepoda of Chiekong and Zaikong Rivers, Kwantung Province, China. Acta Zoologica Sinica 15(4):571-596. (xii-1996, Chinese with English summary).
page(s): :577 [details] Available for editors
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Breckenridge, J.K. , S.M. Bollens & G. Rollwagen-Bollens. (2014). Plankton assemblage variability in a river-dominated temperate estuary during late spring (high-flow) and late summer (low-flow) periods. <em>Estuaries and Coasts.</em> 38(1):93-103. [online May 2014]., available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-014-9820-7 [details] Available for editors
additional source Emerson, J.E., S.M. Bollens & T.D. Counihan. (2015). Seasonal dynamics of zooplankton in Columbia-Snake River reservoirs, with special emphasis on the invasive copepod Pseudodiaptomus forbesi. Aquatic Invasions, 10(1):25-40., available online at https://doi.org/10.3391/ai.2015.10.1.03 [details] Available for editors
additional source Bowen, A., G. Rollwagen-Bollens, S.M. Bollens & J. Zimmerman. (2015). Feeding of the invasive copepod Pseudodiaptomus forbesi on natural microplankton assemblages within the lower Columbia River. Journal Of Plankton Research, 37(6):1089-1094., available online at https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbv078 [details] Available for editors
additional source Borutzky, E.V. (1960). Opredelitel' svobodnozhivushchikh presnovodnykh veslonogikh rakov SSSR i sopredel'nykh stran po fragmentam v kishechnikakh ryb. (Key for determining the free-living freshwater Copepoda of the USSR and neighboring countries, from fragments in fish stomachs. <em>Akademiya Nauk SSSR, Moscow.</em> 1-217, figs. 1-77.
page(s): :22, fig.4-5 [details] Available for editors
additional source Gearty, A.J., T.R. Ignoffo, A.M. Slaughter & W.J. Kimmerer. (2021). Growth and reproductive rates of the dominant copepod Pseudodiaptomus forbesi in response to environmental factors and habitat type in the northern San Francisco Estuary. <em>Aquatic Ecology.</em> 55(3):1-25. MAY 2021., available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-021-09863-4 [details] Available for editors
additional source Yelton, R. A.M. Slaugher & W.J. Kimmerer. (2022). Diel Behaviors of Zooplankton Interact with Tidal Patterns to Drive Spatial Subsidies in the Northern San Francisco Estuary. <em>Estuaries and Coasts.</em> , available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-021-01036-8 [details] Available for editors
additional source Gearty, A.J. (2020). Mechanisms controlling productivity of a calanoid copepod in northern San Francisco estuary. <em>M.Sc. Thesis, San Francisco State University, San Francisco, California, USA.</em> 45 pp., available online at https://doi.org/10.46569/20.500.12680/s1784r547 [details] Available for editors
additional source Hartman, R. (2019). 24 Hour Bugs: Tidal and diel changes in zooplankton distribution in the Sacramento River. <em>Interagency Ecological Program for the San Francisco Estuary. IEP Newsletter.</em> 34(1):11-22., available online at https://nrm.dfg.ca.gov/FileHandler.ashx?DocumentID=184974 [details] Available for editors
additional source Kayfetz, K.R. (2014). Biotic vs. abiotic effects on distribution of the estuarine copepod Pseudodiaptomus forbesi. <em>M.Sc. Thesis, San Francisco State University, San Francisco, California, USA.</em> , available online at http://hdl.handle.net/10211.3/131290 [details]
ecology source Brun, P., M.R. Payne & T. Kiørboe. (2017). A trait database for marine copepods. <em>Earth System Science Data.</em> 9(1):99-113., available online at https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-9-99-2017 [details] Available for editors
 Present
Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio
Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
Marine Planktonic Copepods (Banyuls/OOB/UPMC/CNRS) Note: Including taxonomic identification plates, remarks, geographic distribution, ecological information & reference list
To Barcode of Life (144 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (6 publications)
To European Nucleotide Archive (ENA)
To GenBank (145 nucleotides; 145 proteins)
To GenBank (145 nucleotides; 145 proteins) (from synonym Schmackeria forbesi Poppe & Richard, 1890)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Arthropoda Collection (5 records)
To ITIS
To Barcode of Life (144 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (6 publications)
To European Nucleotide Archive (ENA)
To GenBank (145 nucleotides; 145 proteins)
To GenBank (145 nucleotides; 145 proteins) (from synonym Schmackeria forbesi Poppe & Richard, 1890)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Arthropoda Collection (5 records)
To ITIS